Filter
Associated Lab
- Remove Rubin Lab filter Rubin Lab
Publication Date
Type of Publication
2 Publications
Showing 1-2 of 2 resultsExogenous DNA sequences were introduced into the Drosophila germ line. A rosy transposon (ry1), constructed by inserting a chromosomal DNA fragment containing the wild-type rosy gene into a P transposable element, transformed germ line cells in 20 to 50 percent of the injected rosy mutant embryos. Transformants contained one or two copies of chromosomally integrated, intact ry1 that were stably inherited in subsequent generations. These transformed flies had wild-type eye color indicating that the visible genetic defect in the host strain could be fully and permanently corrected by the transferred gene. To demonstrate the generality of this approach, a DNA segment that does not confer a recognizable phenotype on recipients was also transferred into germ line chromosomes.
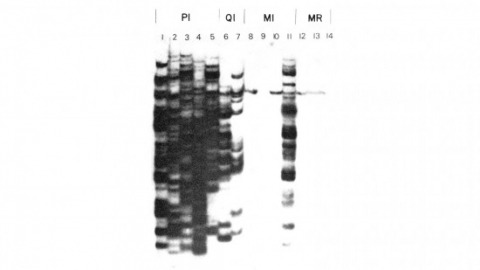
We have shown previously that four of five white mutant alleles arising in P-M dysgenic hybrids result from the insertion of strongly homologous DNA sequence elements. We have named these P elements. We report that P elements are present in 30-50 copies per haploid genome in all P strains examined and apparently are missing entirely from all M strains examined, with one exception. Furthermore, members of the P family apparently transpose frequently in P-M dysgenic hybrids; chromosomes descendant from P-M dysgenic hybrids frequently show newly acquired P elements. Finally, the strain-specific breakpoint hotspots for the rearrangement of the pi 2 P X chromosome occurring in P-M dysgenic hybrids are apparently sites of residence of P elements. These observations strongly support the P factor hypothesis for the mechanistic basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis.