Filter
Associated Lab
- Baker Lab (2) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (3) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (2) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (1) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (1) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (3) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (2) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Harris Lab (1) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Hess Lab (2) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (2) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (1) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Keller Lab (2) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Looger Lab (6) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (3) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (2) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (2) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (2) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (1) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (3) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (1) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (3) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (1) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (7) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Truman Lab (4) Apply Truman Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Associated Support Team
Publication Date
- December 2010 (3) Apply December 2010 filter
- November 2010 (4) Apply November 2010 filter
- October 2010 (5) Apply October 2010 filter
- September 2010 (3) Apply September 2010 filter
- August 2010 (7) Apply August 2010 filter
- July 2010 (2) Apply July 2010 filter
- June 2010 (6) Apply June 2010 filter
- May 2010 (3) Apply May 2010 filter
- April 2010 (5) Apply April 2010 filter
- March 2010 (1) Apply March 2010 filter
- February 2010 (6) Apply February 2010 filter
- January 2010 (16) Apply January 2010 filter
- Remove 2010 filter 2010
61 Janelia Publications
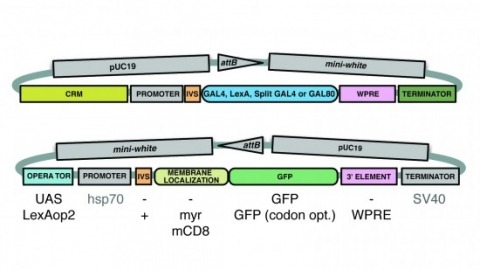
Showing 11-20 of 61 resultsA wide variety of biological experiments rely on the ability to express an exogenous gene in a transgenic animal at a defined level and in a spatially and temporally controlled pattern. We describe major improvements of the methods available for achieving this objective in Drosophila melanogaster. We have systematically varied core promoters, UTRs, operator sequences, and transcriptional activating domains used to direct gene expression with the GAL4, LexA, and Split GAL4 transcription factors and the GAL80 transcriptional repressor. The use of site-specific integration allowed us to make quantitative comparisons between different constructs inserted at the same genomic location. We also characterized a set of PhiC31 integration sites for their ability to support transgene expression of both drivers and responders in the nervous system. The increased strength and reliability of these optimized reagents overcome many of the previous limitations of these methods and will facilitate genetic manipulations of greater complexity and sophistication.
Reconstructing neuronal circuits at the level of synapses is a central problem in neuroscience, and the focus of the nascent field of connectomics. Previously used to reconstruct the C. elegans wiring diagram, serial-section transmission electron microscopy (ssTEM) is a proven technique for the task. However, to reconstruct more complex circuits, ssTEM will require the automation of image processing. We review progress in the processing of electron microscopy images and, in particular, a semi-automated reconstruction pipeline deployed at Janelia. Drosophila circuits underlying identified behaviors are being reconstructed in the pipeline with the goal of generating a complete Drosophila connectome.
Classical studies have related the spiking of selected neocortical neurons to behavior, but little is known about activity sampled from the entire neural population. We recorded from neurons selected independent of spiking, using cell-attached recordings and two-photon calcium imaging, in the barrel cortex of mice performing an object localization task. Spike rates varied across neurons, from silence to >60 Hz. Responses were diverse, with some neurons showing large increases in spike rate when whiskers contacted the object. Nearly half the neurons discriminated object location; a small fraction of neurons discriminated perfectly. More active neurons were more discriminative. Layer (L) 4 and L5 contained the highest fractions of discriminating neurons (\~{}63% and 79%, respectively), but a few L2/3 neurons were also highly discriminating. Approximately 13,000 spikes per activated barrel column were available to mice for decision making. Coding of object location in the barrel cortex is therefore highly redundant.
Complete reconstructions of vertebrate neuronal circuits on the synaptic level require new approaches. Here, serial section transmission electron microscopy was automated to densely reconstruct four volumes, totaling 670 μm(3), from the rat hippocampus as proving grounds to determine when axo-dendritic proximities predict synapses. First, in contrast with Peters’ rule, the density of axons within reach of dendritic spines did not predict synaptic density along dendrites because the fraction of axons making synapses was variable. Second, an axo-dendritic touch did not predict a synapse; nevertheless, the density of synapses along a hippocampal dendrite appeared to be a universal fraction, 0.2, of the density of touches. Finally, the largest touch between an axonal bouton and spine indicated the site of actual synapses with about 80% precision but would miss about half of all synapses. Thus, it will be difficult to predict synaptic connectivity using data sets missing ultrastructural details that distinguish between axo-dendritic touches and bona fide synapses.
The need for optical sectioning in bio-imaging has amongst others led to the development of the two-photon scanning microscopy. However, this comes with some intrinsic fundamental limitations in the temporal domain as the focused spot has to be scanned mechanically in the sample plane. Hence for a large number of biological applications where imaging speed is a limiting factor, it would be significantly advantageous to generate widefield excitations with an optical sectioning comparable to the two-photon scanning microscopy. Recently by using the technique of temporal focusing it was shown that high axial resolution widefield excitation can be generated in picosecond time scales without any mechanical moving parts. However the achievable axial resolution is still well above that of a two-photon scanning microscope. Here we demonstrate a new ultrafast widefield two-photon imaging technique termed Multifocal Temporal Focusing (MUTEF) which relies on the generation of a set of diffraction limited beams produced by an Echelle grating that scan across a second tilted diffraction grating in picosecond time scale, generating a widefield excitation area with an axial resolution comparable to a two-photon scanning microscope. Using this method we have shown widefield two-photon imaging on fixed biological samples with an axial sectioning with a FWHM of 0.85 μm.
Drosophila brains contain numerous neurons that form complex circuits. These neurons are derived in stereotyped patterns from a fixed number of progenitors, called neuroblasts, and identifying individual neurons made by a neuroblast facilitates the reconstruction of neural circuits. An improved MARCM (mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker) technique, called twin-spot MARCM, allows one to label the sister clones derived from a common progenitor simultaneously in different colors. It enables identification of every single neuron in an extended neuronal lineage based on the order of neuron birth. Here we report the first example, to our knowledge, of complete lineage analysis among neurons derived from a common neuroblast that relay olfactory information from the antennal lobe (AL) to higher brain centers. By identifying the sequentially derived neurons, we found that the neuroblast serially makes 40 types of AL projection neurons (PNs). During embryogenesis, one PN with multi-glomerular innervation and 18 uniglomerular PNs targeting 17 glomeruli of the adult AL are born. Many more PNs of 22 additional types, including four types of polyglomerular PNs, derive after the neuroblast resumes dividing in early larvae. Although different offspring are generated in a rather arbitrary sequence, the birth order strictly dictates the fate of each post-mitotic neuron, including the fate of programmed cell death. Notably, the embryonic progenitor has an altered temporal identity following each self-renewing asymmetric cell division. After larval hatching, the same progenitor produces multiple neurons for each cell type, but the number of neurons for each type is tightly regulated. These observations substantiate the origin-dependent specification of neuron types. Sequencing neuronal lineages will not only unravel how a complex brain develops but also permit systematic identification of neuron types for detailed structure and function analysis of the brain.
Changes in behavioral state modify neural activity in many systems. In some vertebrates such modulation has been observed and interpreted in the context of attention and sensorimotor coordinate transformations. Here we report state-dependent activity modulations during walking in a visual-motor pathway of Drosophila. We used two-photon imaging to monitor intracellular calcium activity in motion-sensitive lobula plate tangential cells (LPTCs) in head-fixed Drosophila walking on an air-supported ball. Cells of the horizontal system (HS)–a subgroup of LPTCs–showed stronger calcium transients in response to visual motion when flies were walking rather than resting. The amplified responses were also correlated with walking speed. Moreover, HS neurons showed a relatively higher gain in response strength at higher temporal frequencies, and their optimum temporal frequency was shifted toward higher motion speeds. Walking-dependent modulation of HS neurons in the Drosophila visual system may constitute a mechanism to facilitate processing of higher image speeds in behavioral contexts where these speeds of visual motion are relevant for course stabilization.
To study the complex synaptic interactions underpinning dendritic information processing in single neurons, experimenters require methods to mimic presynaptic neurotransmitter release at multiple sites with no physiological damage. We show that laser scanning systems built around large-aperture acousto-optic deflectors and high numerical aperture objective lenses provide the sub-millisecond, sub-micron precision necessary to achieve physiological, exogenous synaptic stimulation. Our laser scanning systems can produce the sophisticated spatio-temporal patterns of synaptic input that are necessary to investigate single-neuron dendritic physiology.
Mitochondria are difficult targets for microscopy because of their small size and highly compartmentalized, membranous interior. Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy methods have recently been developed that exceed the historical limits of optical imaging. Here we outline considerations and techniques in preparing to image the relative location of mitochondrial proteins using photoactivated localization microscopy (PALM). PALM and similar methods have the capacity to dramatically increase our ability to image proteins within mitochondria, and to expand our knowledge of the location of macromolecules beyond the current limits of immunoEM.
The neuropile of the Drosophila brain is subdivided into anatomically discrete compartments. Compartments are rich in terminal neurite branching and synapses; they are the neuropile domains in which signal processing takes place. Compartment boundaries are defined by more or less dense layers of glial cells as well as long neurite fascicles. These fascicles are formed during the larval period, when the approximately 100 neuronal lineages that constitute the Drosophila central brain differentiate. Each lineage forms an axon tract with a characteristic trajectory in the neuropile; groups of spatially related tracts congregate into the brain fascicles that can be followed from the larva throughout metamorphosis into the adult stage. Here we provide a map of the adult brain compartments and the relevant fascicles defining compartmental boundaries. We have identified the neuronal lineages contributing to each fascicle, which allowed us to compare compartments of the larval and adult brain directly. Most adult compartments can be recognized already in the early larval brain, where they form a "protomap" of the later adult compartments. Our analysis highlights the morphogenetic changes shaping the Drosophila brain; the data will be important for studies that link early-acting genetic mechanisms to the adult neuronal structures and circuits controlled by these mechanisms.