Filter
Associated Lab
Publication Date
2 Janelia Publications
Showing 1-2 of 2 resultsMany animals maintain an internal representation of their heading as they move through their surroundings. Such a compass representation was recently discovered in a neural population in the Drosophila melanogaster central complex, a brain region implicated in spatial navigation. Here, we use two-photon calcium imaging and electrophysiology in head-fixed walking flies to identify a different neural population that conjunctively encodes heading and angular velocity, and is excited selectively by turns in either the clockwise or counterclockwise direction. We show how these mirror-symmetric turn responses combine with the neurons' connectivity to the compass neurons to create an elegant mechanism for updating the fly's heading representation when the animal turns in darkness. This mechanism, which employs recurrent loops with an angular shift, bears a resemblance to those proposed in theoretical models for rodent head direction cells. Our results provide a striking example of structure matching function for a broadly relevant computation.
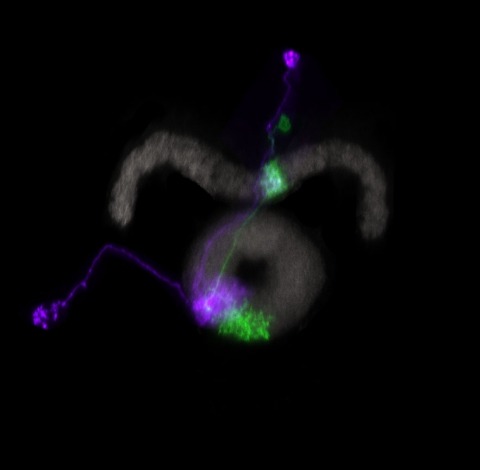
Animals exhibit a behavioral response to novel sensory stimuli about which they have no prior knowledge. We have examined the neural and behavioral correlates of novelty and familiarity in the olfactory system of Drosophila. Novel odors elicit strong activity in output neurons (MBONs) of the α'3 compartment of the mushroom body that is rapidly suppressed upon repeated exposure to the same odor. This transition in neural activity upon familiarization requires odor-evoked activity in the dopaminergic neuron innervating this compartment. Moreover, exposure of a fly to novel odors evokes an alerting response that can also be elicited by optogenetic activation of α'3 MBONs. Silencing these MBONs eliminates the alerting behavior. These data suggest that the α'3 compartment plays a causal role in the behavioral response to novel and familiar stimuli as a consequence of dopamine-mediated plasticity at the Kenyon cell-MBONα'3 synapse.