Filter
Associated Lab
- Ahrens Lab (4) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (2) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Branson Lab (1) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (3) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (5) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (3) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (1) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (3) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Harris Lab (6) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (1) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (9) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (2) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (2) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (4) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (3) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (2) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (1) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (20) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (1) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (2) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (1) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (2) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Romani Lab (5) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (3) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (2) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (13) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (3) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (4) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Remove Svoboda Lab filter Svoboda Lab
- Tillberg Lab (3) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Turner Lab (3) Apply Turner Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Publication Date
- 2023 (5) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (6) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (7) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (5) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (14) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (11) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (9) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (8) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (9) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (7) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (10) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (9) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (7) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (7) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (9) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (6) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (3) Apply 2007 filter
- 2005 (2) Apply 2005 filter
- 2004 (1) Apply 2004 filter
Type of Publication
135 Publications
Showing 51-60 of 135 resultsNeurons relevant to a particular behavior are often widely dispersed across the brain. To record activity in groups of individual neurons that might be distributed across large distances, neuroscientists and optical engineers have been developing a new type of microscope called a mesoscope. Mesoscopes have high spatial resolution and a large field of view. This Q&A will discuss this exciting new technology, highlighting a particular instrument, the two-photon random access mesoscope (2pRAM).
The world view of rodents is largely determined by sensation on two length scales. One is within the animal's peri-personal space. Sensorimotor control on this scale involves active movements of the nose, tongue, head, and vibrissa, along with sniffing to determine olfactory clues. The second scale involves the detection of more distant space through vision and audition; these detection processes also impact repositioning of the head, eyes, and ears. Here we focus on orofacial motor actions, primarily vibrissa-based touch but including nose twitching, head bobbing, and licking, that control sensation at short, peri-personal distances. The orofacial nuclei for control of the motor plants, as well as primary and secondary sensory nuclei associated with these motor actions, lie within the hindbrain. The current data support three themes: First, the position of the sensors is determined by the summation of two drive signals, i.e., a fast rhythmic component and an evolving orienting component. Second, the rhythmic component is coordinated across all orofacial motor actions and is phase-locked to sniffing as the animal explores. Reverse engineering reveals that the preBötzinger inspiratory complex provides the reset to the relevant premotor oscillators. Third, direct feedback from somatosensory trigeminal nuclei can rapidly alter motion of the sensors. This feedback is disynaptic and can be tuned by high-level inputs. The elucidation of synergistic coordination of orofacial motor actions to form behaviors, beyond that of a common rhythmic component, represents a work in progress that encompasses feedback through the midbrain and forebrain as well as hindbrain areas.
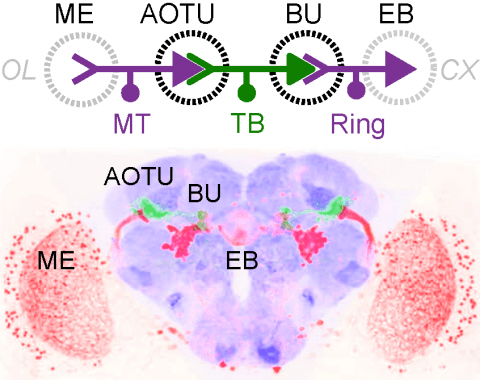
Many animals orient using visual cues, but how a single cue is selected from among many is poorly understood. Here we show that Drosophila ring neurons—central brain neurons implicated in navigation—display visual stimulus selection. Using in vivo two-color two-photon imaging with genetically encoded calcium indicators, we demonstrate that individual ring neurons inherit simple-cell-like receptive fields from their upstream partners. Stimuli in the contralateral visual field suppressed responses to ipsilateral stimuli in both populations. Suppression strength depended on when and where the contralateral stimulus was presented, an effect stronger in ring neurons than in their upstream inputs. This history-dependent effect on the temporal structure of visual responses, which was well modeled by a simple biphasic filter, may determine how visual references are selected for the fly's internal compass. Our approach highlights how two-color calcium imaging can help identify and localize the origins of sensory transformations across synaptically connected neural populations.
During active somatosensation, neural signals expected from movement of the sensors are suppressed in the cortex, whereas information related to touch is enhanced. This tactile suppression underlies low-noise encoding of relevant tactile features and the brain's ability to make fine tactile discriminations. Layer (L) 4 excitatory neurons in the barrel cortex, the major target of the somatosensory thalamus (VPM), respond to touch, but have low spike rates and low sensitivity to the movement of whiskers. Most neurons in VPM respond to touch and also show an increase in spike rate with whisker movement. Therefore, signals related to self-movement are suppressed in L4. Fast-spiking (FS) interneurons in L4 show similar dynamics to VPM neurons. Stimulation of halorhodopsin in FS interneurons causes a reduction in FS neuron activity and an increase in L4 excitatory neuron activity. This decrease of activity of L4 FS neurons contradicts the "paradoxical effect" predicted in networks stabilized by inhibition and in strongly-coupled networks. To explain these observations, we constructed a model of the L4 circuit, with connectivity constrained by in vitro measurements. The model explores the various synaptic conductance strengths for which L4 FS neurons actively suppress baseline and movement-related activity in layer 4 excitatory neurons. Feedforward inhibition, in concert with recurrent intracortical circuitry, produces tactile suppression. Synaptic delays in feedforward inhibition allow transmission of temporally brief volleys of activity associated with touch. Our model provides a mechanistic explanation of a behavior-related computation implemented by the thalamocortical circuit.
Activity in the mouse anterior lateral motor cortex (ALM) instructs directional movements, often seconds before movement initiation. It is unknown whether this preparatory activity is localized to ALM or widely distributed within motor cortex. Here we imaged activity across motor cortex while mice performed a whisker-based object localization task with a delayed, directional licking response. During tactile sensation and the delay epoch, object location was represented in motor cortex areas that are medial and posterior relative to ALM, including vibrissal motor cortex. Preparatory activity appeared first in deep layers of ALM, seconds before the behavioral response, and remained localized to ALM until the behavioral response. Later, widely distributed neurons represented the outcome of the trial. Cortical area was more predictive of neuronal selectivity than laminar location or axonal projection target. Motor cortex therefore represents sensory, motor, and outcome information in a spatially organized manner.
Persistent neural activity maintains information that connects past and future events. Models of persistent activity often invoke reverberations within local cortical circuits, but long-range circuits could also contribute. Neurons in the mouse anterior lateral motor cortex (ALM) have been shown to have selective persistent activity that instructs future actions. The ALM is connected bidirectionally with parts of the thalamus, including the ventral medial and ventral anterior-lateral nuclei. We recorded spikes from the ALM and thalamus during tactile discrimination with a delayed directional response. Here we show that, similar to ALM neurons, thalamic neurons exhibited selective persistent delay activity that predicted movement direction. Unilateral photoinhibition of delay activity in the ALM or thalamus produced contralesional neglect. Photoinhibition of the thalamus caused a short-latency and near-complete collapse of ALM activity. Similarly, photoinhibition of the ALM diminished thalamic activity. Our results show that the thalamus is a circuit hub in motor preparation and suggest that persistent activity requires reciprocal excitation across multiple brain areas.
Neurons and neural networks often extend hundreds of micrometers in three dimensions. Capturing the calcium transients associated with their activity requires volume imaging methods with subsecond temporal resolution. Such speed is a challenge for conventional two-photon laser-scanning microscopy, because it depends on serial focal scanning in 3D and indicators with limited brightness. Here we present an optical module that is easily integrated into standard two-photon laser-scanning microscopes to generate an axially elongated Bessel focus, which when scanned in 2D turns frame rate into volume rate. We demonstrated the power of this approach in enabling discoveries for neurobiology by imaging the calcium dynamics of volumes of neurons and synapses in fruit flies, zebrafish larvae, mice and ferrets in vivo. Calcium signals in objects as small as dendritic spines could be resolved at video rates, provided that the samples were sparsely labeled to limit overlap in their axially projected images.
The neuronal circuits defined by the axonal projections of pyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex are responsible for processing sensory and other information to plan and execute behavior. Subtypes of cortical pyramidal neurons are organized across layers, with those in different layers distinguished by their patterns of axonal projections and connectivity. For example, those in layers 2 and 3 project between cortical areas to integrate sensory and other information with motor areas; while those in layers 5 and 6 also integrate information between cortical areas, but also project to subcortical structures involved in the generation of behavior. Recent advances in neuroanatomical techniques allow one to target specific subtypes of cortical pyramidal neurons and label both their inputs and projections. Combining these methods with neurophysiological recording techniques and newly introduced atlases of the mouse brain provide the opportunity to achieve a detailed view of the organization of cerebral cortical circuits.
Neuroscience research is becoming increasingly more collaborative and interdisciplinary with partnerships between industry and academia and insights from fields beyond neuroscience. In the age of institutional initiatives and multi-investigator collaborations, scientists from around the world shared their perspectives on the effectiveness of large-scale collaborations versus single-lab, hypothesis-driven science.
We rely on movement to explore the environment, for example, by palpating an object. In somatosensory cortex, activity related to movement of digits or whiskers is suppressed, which could facilitate detection of touch. Movement-related suppression is generally assumed to involve corollary discharges. Here we uncovered a thalamocortical mechanism in which cortical fast-spiking interneurons, driven by sensory input, suppress movement-related activity in layer 4 (L4) excitatory neurons. In mice locating objects with their whiskers, neurons in the ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) fired in response to touch and whisker movement. Cortical L4 fast-spiking interneurons inherited these responses from VPM. In contrast, L4 excitatory neurons responded mainly to touch. Optogenetic experiments revealed that fast-spiking interneurons reduced movement-related spiking in excitatory neurons, enhancing selectivity for touch-related information during active tactile sensation. These observations suggest a fundamental computation performed by the thalamocortical circuit to accentuate salient tactile information.