Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (1) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (53) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (40) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (19) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (101) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (8) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (14) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (50) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (36) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (45) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (10) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (14) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (8) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (32) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (21) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (38) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (4) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (15) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (7) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (31) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (16) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (38) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (59) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (34) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (53) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (13) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (23) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (74) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (2) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (42) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (1) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (13) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (8) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (61) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (2) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (137) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (29) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (19) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (4) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (97) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (1) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (58) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (137) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (31) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (12) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (6) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (6) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (1) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (36) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (5) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (7) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (4) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (45) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (20) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (31) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (105) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (46) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (1) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (36) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (50) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (1) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (31) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (18) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (37) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (57) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (73) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (47) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (32) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (131) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (9) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (18) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (17) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (58) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (39) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (27) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (7) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (3) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (21) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (6) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wu Lab (8) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (26) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (5) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (12) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (3) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (11) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (53) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (49) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (46) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (4) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (18) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (26) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (45) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Publication Date
- 2025 (126) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (215) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (159) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (167) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (175) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (177) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (177) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (206) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (186) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (191) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (195) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (190) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (136) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (112) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (98) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (61) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (56) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (40) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (21) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (3) Apply 2006 filter
Type of Publication
- Remove Janelia filter Janelia
2691 Publications
Showing 1991-2000 of 2691 resultsHolometabolous insects pass through a sedentary pupal stage and often choose a location for pupation that is different from the site of larval feeding. We have characterized a difference in pupariation site choice within and between sibling species of Drosophila. We found that, in nature, Drosophila sechellia pupariate within their host fruit, Morinda citrifolia, and that they perform this behavior in laboratory assays. In contrast, in the laboratory, geographically diverse strains of Drosophila simulans vary in their pupariation site preference; D. simulans lines from the ancestral range in southeast Africa pupariate on fruit, or a fruit substitute, whereas populations from Europe or the New World select sites off of fruit. We explored the genetic basis for the evolved preference in puariation site preference by performing quantitative trait locus mapping within and between species. We found that the interspecific difference is controlled largely by loci on chromosomes X and II. In contrast, variation between two strains of D. simulans appears to be highly polygenic, with the majority of phenotypic effects due to loci on chromosome III. These data address the genetic basis of how new traits arise as species diverge and populations disperse.
BACKGROUND: In most species of aphid, female nymphs develop into either sexual or asexual adults depending on the length of the photoperiod to which their mothers were exposed. The progeny of these sexual and asexual females, in turn, develop in dramatically different ways. The fertilized oocytes of sexual females begin embryogenesis after being deposited on leaves (oviparous development) while the oocytes of asexual females complete embryogenesis within the mother (viviparous development). Compared with oviparous development, viviparous development involves a smaller transient oocyte surrounded by fewer somatic epithelial cells and a smaller early embryo that comprises fewer cells. To investigate whether patterning mechanisms differ between the earliest stages of the oviparous and viviparous modes of pea aphid development, we examined the expression of pea aphid orthologs of genes known to specify embryonic termini in other insects. RESULTS: Here we show that pea aphid oviparous ovaries express torso-like in somatic posterior follicle cells and activate ERK MAP kinase at the posterior of the oocyte. In addition to suggesting that some posterior features of the terminal system are evolutionarily conserved, our detection of activated ERK in the oocyte, rather than in the embryo, suggests that pea aphids may transduce the terminal signal using a mechanism distinct from the one used in Drosophila. In contrast with oviparous development, the pea aphid version of the terminal system does not appear to be used during viviparous development, since we did not detect expression of torso-like in the somatic epithelial cells that surround either the oocyte or the blastoderm embryo and we did not observe restricted activated ERK in the oocyte. CONCLUSIONS: We suggest that while oviparous oocytes and embryos may specify posterior fate through an aphid terminal system, viviparous oocytes and embryos employ a different mechanism, perhaps one that does not rely on an interaction between the oocyte and surrounding somatic cells. Together, these observations provide a striking example of a difference in the fundamental events of early development that is both environmentally induced and encoded by the same genome.
In eukaryotic cells, post-translational histone modifications have an important role in gene regulation. Starting with early work on histone acetylation, a variety of residue-specific modifications have now been linked to RNA polymerase II (RNAP2) activity, but it remains unclear if these markers are active regulators of transcription or just passive byproducts. This is because studies have traditionally relied on fixed cell populations, meaning temporal resolution is limited to minutes at best, and correlated factors may not actually be present in the same cell at the same time. Complementary approaches are therefore needed to probe the dynamic interplay of histone modifications and RNAP2 with higher temporal resolution in single living cells. Here we address this problem by developing a system to track residue-specific histone modifications and RNAP2 phosphorylation in living cells by fluorescence microscopy. This increases temporal resolution to the tens-of-seconds range. Our single-cell analysis reveals histone H3 lysine-27 acetylation at a gene locus can alter downstream transcription kinetics by as much as 50%, affecting two temporally separate events. First acetylation enhances the search kinetics of transcriptional activators, and later the acetylation accelerates the transition of RNAP2 from initiation to elongation. Signatures of the latter can be found genome-wide using chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing. We argue that this regulation leads to a robust and potentially tunable transcriptional response.
Sensorimotor control in vertebrates relies on internal models. When extending an arm to reach for an object, the brain uses predictive models of both limb dynamics and target properties. Whether invertebrates use such models remains unclear. Here we examine to what extent prey interception by dragonflies (Plathemis lydia), a behaviour analogous to targeted reaching, requires internal models. By simultaneously tracking the position and orientation of a dragonfly's head and body during flight, we provide evidence that interception steering is driven by forward and inverse models of dragonfly body dynamics and by models of prey motion. Predictive rotations of the dragonfly's head continuously track the prey's angular position. The head-body angles established by prey tracking appear to guide systematic rotations of the dragonfly's body to align it with the prey's flight path. Model-driven control thus underlies the bulk of interception steering manoeuvres, while vision is used for reactions to unexpected prey movements. These findings illuminate the computational sophistication with which insects construct behaviour.
Stoichiometric labeling of endogenous synaptic proteins for high-contrast live-cell imaging in brain tissue remains challenging. Here, we describe a conditional mouse genetic strategy termed endogenous labeling via exon duplication (ENABLED), which can be used to fluorescently label endogenous proteins with near ideal properties in all neurons, a sparse subset of neurons, or specific neuronal subtypes. We used this method to label the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 with mVenus without overexpression side effects. We demonstrated that mVenus-tagged PSD-95 is functionally equivalent to wild-type PSD-95 and that PSD-95 is present in nearly all dendritic spines in CA1 neurons. Within spines, while PSD-95 exhibited low mobility under basal conditions, its levels could be regulated by chronic changes in neuronal activity. Notably, labeled PSD-95 also allowed us to visualize and unambiguously examine otherwise-unidentifiable excitatory shaft synapses in aspiny neurons, such as parvalbumin-positive interneurons and dopaminergic neurons. Our results demonstrate that the ENABLED strategy provides a valuable new approach to study the dynamics of endogenous synaptic proteins in vivo.
The hemoglobinopathies, such as β-thalassemia and sickle cell anemia (SCA), are characterized by mutations of the β-globin gene resulting in either decreased or functionally abnormal hemoglobin (Hb) production. As bone marrow transplant is the only curative option for these patients, there is a strong need for new therapeutic approaches. Both β-thalassemia and SCA represent ideal targets for gene therapy since introduction of a normal β-globin gene can ameliorate the phenotype, as we and others have shown previously. Overcoming the developmental silencing of the fetal γ-globin gene represents an additional approach for the treatment of hemoglobinopathies. Here, we directly compare a recently established approach to activate the γ-globin gene using forced chromatin looping with pharmacologic approaches to raise γ-globin expression. The β-type globin genes are activated through dynamic interactions with a distal upstream enhancer, the locus control region (LCR). The LCR physically contacts the developmental stage appropriate globin gene via chromatin looping, a process partially dependent on the protein Ldb1. Previously, we have shown that tethering Ldb1 to the murine β-globin promoter with a custom designed zinc finger protein (ZF-Ldb1) can induce loop formation and β-globin transcription in an erythroid cell line (Deng et al., 2012). Further work showed that forced chromatin looping can be exploited to potently reactivate fetal globin gene expression in adult human erythroid cells (Deng et al., 2014). Here we compared the efficacy and toxicity of ZF-Ldb1 to pharmacologic compounds that induce HbF in cultured hematopoietic stem progenitor cell-derived erythroid cultures from normal and SCA donors. ZF-Ldb1 increased HbF synthesis in SCA erythroid cells (N=8) up to 86% and, concurrently, reduced sickle Hb (HbS) below 15%, consistent with previous studies of erythroid cells from normal probands. Preliminary results obtained from treating SCA specimens (N=3) show that the induction of HbF in cells treated with ZF-Ldb1 is twice as high (+35.55% ± 8.34%, at a dose of ~ one ZF-Ldb1 transgene copy per cell) as that observed using pomalidomide (+16.50% ± 14.57%, 20μM) and decitabine (+15.60% ± 12.36%, 0.5μM). Tranylcypromine and hydroxyurea showed the lowest HbF increase (+9.67% ± 3.26% and +5.06 ± 2.82%, 1.5μM and 150μM respectively). Importantly, decitabine and pomalidomide treatment lowered cell viability to 39% and 26%, respectively, while ZF-Ldb1 expressing cells retained normal viability similar to control populations. In related experiments, we are comparing the expression of a battery of genes known to regulate HbF levels (BCL11A, SOX6, KLF1 and C-Myb) in normal and SCA derived erythroid cells treated with ZF-Ldb1 or HbF inducers and compared to controls. Preliminary analyses indicate altered expression of KLF1 in SCA versus normal cells, consistent with a superior response of SCA cells to HbF induction. In conclusion, lentiviral-mediated ZF-Ldb1 gene transfer appears superior to pharmacologic compounds in terms of efficacy and cell viability further supporting suitability for the reactivation of HbF in SCA erythroid cells.
Synaptic connectivity and molecular composition provide a blueprint for information processing in neural circuits. Detailed structural analysis of neural circuits requires nanometer resolution, which can be obtained with serial-section electron microscopy. However, this technique remains challenging for reconstructing molecularly defined synapses. We used a genetically encoded synaptic marker for electron microscopy (GESEM) based on intra-vesicular generation of electron-dense labeling in axonal boutons. This approach allowed the identification of synapses from Cre recombinase-expressing or GAL4-expressing neurons in the mouse and fly with excellent preservation of ultrastructure. We applied this tool to visualize long-range connectivity of AGRP and POMC neurons in the mouse, two molecularly defined hypothalamic populations that are important for feeding behavior. Combining selective ultrastructural reconstruction of neuropil with functional and viral circuit mapping, we characterized some basic features of circuit organization for axon projections of these cell types. Our findings demonstrate that GESEM labeling enables long-range connectomics with molecularly defined cell types.
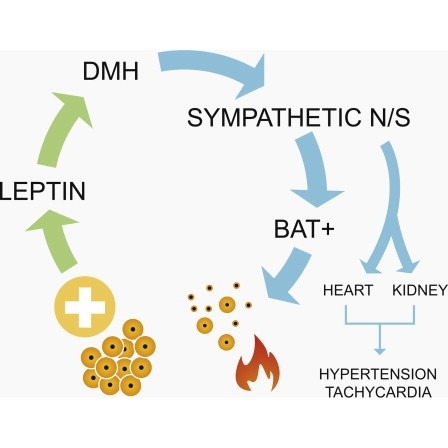
Obesity is associated with increased blood pressure (BP), which in turn increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. We found that the increase in leptin levels seen in diet-induced obesity (DIO) drives an increase in BP in rodents, an effect that was not seen in animals deficient in leptin or leptin receptors (LepR). Furthermore, humans with loss-of-function mutations in leptin and the LepR have low BP despite severe obesity. Leptin's effects on BP are mediated by neuronal circuits in the dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH), as blocking leptin with a specific antibody, antagonist, or inhibition of the activity of LepR-expressing neurons in the DMH caused a rapid reduction of BP in DIO mice, independent of changes in weight. Re-expression of LepRs in the DMH of DIO LepR-deficient mice caused an increase in BP. These studies demonstrate that leptin couples changes in weight to changes in BP in mammalian species.
A subclass of fluorescent proteins (FPs), large Stokes shift (LSS) FP, are characterized by increased spread between excitation and emission maxima. We report a photoswitchable variant of a red FP with an LSS, PSLSSmKate, which initially exhibits excitation and emission at 445 and 622 nm, but violet irradiation photoswitches PSLSSmKate into a common red form with excitation and emission at 573 and 621 nm. We characterize spectral, photophysical, and biochemical properties of PSLSSmKate in vitro and in mammalian cells and determine its crystal structure in the LSS form. Mass spectrometry, mutagenesis, and spectroscopy of PSLSSmKate allow us to propose molecular mechanisms for the LSS, pH dependence, and light-induced chromophore transformation. We demonstrate the applicability of PSLSSmKate to superresolution photoactivated localization microscopy and protein dynamics in live cells. Given its promising properties, we expect that PSLSSmKate-like phenotype will be further used for photoactivatable imaging and tracking multiple populations of intracellular objects.
Staphylococcus aureus responds to changing extracellular environments in part by adjusting its proteome through alterations of transcriptional priorities and selective degradation of the preexisting pool of proteins. In Bacillus subtilis, the proteolytic adaptor protein MecA has been shown to play a role in assisting with the proteolytic degradation of proteins involved in competence and the oxidative stress response. However, the targets of TrfA, the MecA homolog in S. aureus, have not been well characterized. In this work, we investigated how TrfA assists chaperones and proteases to regulate the proteolysis of several classes of proteins in S. aureus. By fusing the last 3 amino acids of the SsrA degradation tag to Venus, a rapidly folding yellow fluorescent protein, we obtained both fluorescence-based and Western blot assay-based evidence that TrfA and ClpCP are the adaptor and protease, respectively, responsible for the degradation of the SsrA-tagged protein in S. aureus. Notably, the impact of TrfA on degradation was most prominent during late log phase and early stationary phase, due in part to a combination of transcriptional regulation and proteolytic degradation of TrfA by ClpCP. We also characterized the temporal transcriptional regulation governing TrfA activity, wherein Spx, a redox-sensitive transcriptional regulator degraded by ClpXP, activates trfA transcription while repressing its own promoter. Finally, the scope of TrfA-mediated proteolysis was expanded by identifying TrfA as the adaptor that works with ClpCP to degrade antitoxins in S. aureus. Together, these results indicate that the adaptor TrfA adds temporal nuance to protein degradation by ClpCP in S. aureus.