Filter
Associated Lab
- Ahrens Lab (2) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (1) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Card Lab (1) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (1) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (1) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (2) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (1) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (2) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hess Lab (1) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (1) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (2) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (2) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (1) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (3) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Magee Lab (5) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (1) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (1) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (3) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (1) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (1) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (2) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (2) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (6) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (6) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (3) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (1) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (3) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Publication Date
- December 2006 (4) Apply December 2006 filter
- November 2006 (10) Apply November 2006 filter
- October 2006 (7) Apply October 2006 filter
- September 2006 (7) Apply September 2006 filter
- August 2006 (14) Apply August 2006 filter
- July 2006 (4) Apply July 2006 filter
- June 2006 (7) Apply June 2006 filter
- May 2006 (9) Apply May 2006 filter
- April 2006 (4) Apply April 2006 filter
- March 2006 (12) Apply March 2006 filter
- February 2006 (6) Apply February 2006 filter
- January 2006 (8) Apply January 2006 filter
- Remove 2006 filter 2006
Type of Publication
92 Publications
Showing 31-40 of 92 resultsMammalian mitochondria maintain a small circular genome that encodes RNA and polypeptides that are essential for the generation of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. The mechanism of replication of mammalian mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has recently been a topic of controversy. New evidence has led to a modified strand-displacement model that reconciles much of the current data. This revision stems from a new appreciation for alternative light-strand origins. We consider here some of the potential mechanisms for light-strand origin initiation. We also consider further the susceptibility of branch migration within replicating mtDNA molecules. The existence of alternative light-strand origins and a propensity for branch migration in replicating mtDNA molecules exposes a new array of possible configurations of mtDNA. The assortment and assignment of these forms is relevant to the interpretation of experimental data and may also yield insight into the molecular basis of replication errors.
MARCM (mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker) involves specific labeling of GAL80-minus and GAL4-positive homozygous cells in otherwise heterozygous tissues. Here we demonstrate how the concurrent use of two independent binary transcriptional systems may facilitate complex MARCM studies in the Drosophila nervous system. By fusing LexA with the VP16 acidic activation domain (VP16) or the GAL4 activation domain (GAD), we obtained both GAL80-insensitive and GAL80-suppressible transcriptional factors. LexA::VP16 can mediate MARCM-independent binary transgene induction in mosaic organisms. The incorporation of LexA::GAD into MARCM, which we call dual-expression-control MARCM, permits the induction of distinct transgenes in different patterns among GAL80-minus cells in mosaic tissues. Lineage analysis with dual-expression-control MARCM suggested the presence of neuroglioblasts in the developing optic lobes but did not indicate the production of glia by postembryonic mushroom body neuronal precursors. In addition, dual-expression-control MARCM with a ubiquitous LexA::GAD driver revealed many unidentified cells in the GAL4-GH146-positive projection neuron lineages.
Many neural progenitors, including Drosophila mushroom body (MB) and projection neuron (PN) neuroblasts, sequentially give rise to different subtypes of neurons throughout development. We identified a novel BTB-zinc finger protein, named Chinmo (Chronologically inappropriate morphogenesis), that governs neuronal temporal identity during postembryonic development of the Drosophila brain. In both MB and PN lineages, loss of Chinmo autonomously causes early-born neurons to adopt the fates of late-born neurons from the same lineages. Interestingly, primarily due to a posttranscriptional control, MB neurons born at early developmental stages contain more abundant Chinmo than their later-born siblings. Further, the temporal identity of MB progeny can be transformed toward earlier or later fates by reducing or increasing Chinmo levels, respectively. Taken together, we suggest that a temporal gradient of Chinmo (Chinmo(high) –> Chinmo(low)) helps specify distinct birth order-dependent cell fates in an extended neuronal lineage.
Identifying the genes underlying genetically complex traits is of fundamental importance for medicine, agriculture, and evolutionary biology. However, the level of resolution offered by traditional quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping is usually coarse. We analyze here a trait closely related to fitness, ovariole number. Our initial interspecific mapping between Drosophila sechellia (8 ovarioles/ovary) and D. simulans (15 ovarioles/ovary) identified a major QTL on chromosome 3 and a minor QTL on chromosome 2. To refine the position of the major QTL, we selected 1038 additional recombinants in the region of interest using flanking morphological markers (selective phenotyping). This effort generated approximately one recombination event per gene and increased the mapping resolution by approximately seven times. Our study thus shows that using visible markers to select for recombinants can efficiently increase the resolution of QTL mapping. We resolved the major QTL into two epistatic QTL, QTL3a and QTL3b. QTL3a shows sign epistasis: it has opposite effects in two different genetic backgrounds, the presence vs. the absence of the QTL3b D. sechellia allele. This property of QTL3a allows us to reconstruct the probable order of fixation of the QTL alleles during evolution.
Anemophilous plants described as catapulting pollen explosively into the air have rarely attracted detailed examination. We investigated floral anthesis in a male mulberry tree with high-speed video and a force probe. The stamen was inflexed within the floral bud. Exposure to dry air initially resulted in a gradual movement of the stamen. This caused fine threads to tear at the stomium, ensuring dehiscence of the anther, and subsequently enabled the anther to slip off a restraining pistillode. The sudden release of stored elastic energy in the spring-like filament drove the stamen to straighten in less than 25 μs, and reflex the petals to velocities in excess of half the speed of sound. This is the fastest motion yet observed in biology, and approaches the theoretical physical limits for movements in plants.
Ethanol stimulates the firing activity of midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons, leading to enhanced dopaminergic transmission in the mesolimbic system. This effect is thought to underlie the behavioral reinforcement of alcohol intake. Ethanol has been shown to directly enhance the intrinsic pacemaker activity of DA neurons, yet the cellular mechanism mediating this excitation remains poorly understood. The hyperpolarization-activated cation current, Ih, is known to contribute to the pacemaker firing of DA neurons. To determine the role of Ih in ethanol excitation of DA neurons, we performed patch-clamp recordings in acutely prepared mouse midbrain slices. Superfusion of ethanol increased the spontaneous firing frequency of DA neurons in a reversible fashion. Treatment with ZD7288, a blocker of Ih, irreversibly depressed basal firing frequency and significantly attenuated the stimulatory effect of ethanol on firing. Furthermore, ethanol reversibly augmented Ih amplitude and accelerated its activation kinetics. This effect of ethanol was accompanied by a shift in the voltage dependence of Ih activation to more depolarized potentials and an increase in the maximum Ih conductance. Cyclic AMP mediated the depolarizing shift in Ih activation but not the increase in the maximum conductance. Finally, repeated ethanol treatment in vivo induced downregulation of Ih density in DA neurons and an accompanying reduction in the magnitude of ethanol stimulation of firing. These results suggest an important role of Ih in the reinforcing actions of ethanol and in the neuroadaptations underlying escalation of alcohol consumption associated with alcoholism.
The glycolytic pathway of the hyperthermophilic archaea that belong to the order Thermococcales (Pyrococcus, Thermococcus and Palaeococcus) differs significantly from the canonical Embden-Meyerhof pathway in bacteria and eukarya. This archaeal glycolysis variant consists of several novel enzymes, some of which catalyze unique conversions. Moreover, the enzymes appear not to be regulated allosterically, but rather at transcriptional level. To elucidate details of the gene expression control, the transcription initiation sites of the glycolytic genes in Pyrococcus furiosus have been mapped by primer extension analysis and the obtained promoter sequences have been compared with upstream regions of non-glycolytic genes. Apart from consensus sequences for the general transcription factors (TATA-box and BRE) this analysis revealed the presence of a potential transcription factor binding site (TATCAC-N(5)-GTGATA) in glycolytic and starch utilizing promoters of P. furiosus and several thermococcal species. The absence of this inverted repeat in Pyrococcus abyssi and Pyrococcus horikoshii probably reflects that their reduced catabolic capacity does not require this regulatory system. Moreover, this phyletic pattern revealed a TrmB-like regulator (PF0124 and TK1769) which may be involved in recognizing the repeat. This Thermococcales glycolytic regulon, with more than 20 genes, is the largest regulon that has yet been described for Archaea.
Image diffusion can smooth away noise and small-scale structures while retaining important features, thereby enhancing the performances of many image processing algorithms such as image compression, segmentation and recognition. In this paper, we present a novel diffusion algorithm for which the filtering kernels vary according to the perceptual saliency of boundaries in the input images. The boundary saliency is estimated through a saliency measure which is generally determined by curvature changes, intensity gradient and the interaction of neighboring vectors. The connection between filtering kernels and perceptual saliency makes it possible to remove small-scale structures and preserves significant boundaries adaptively. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is validated by experiments on various medical images including the color Chinese Visible Human data set and gray MRI brain images.
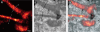
We introduce a method for optically imaging intracellular proteins at nanometer spatial resolution. Numerous sparse subsets of photoactivatable fluorescent protein molecules were activated, localized (to approximately 2 to 25 nanometers), and then bleached. The aggregate position information from all subsets was then assembled into a superresolution image. We used this method–termed photoactivated localization microscopy–to image specific target proteins in thin sections of lysosomes and mitochondria; in fixed whole cells, we imaged vinculin at focal adhesions, actin within a lamellipodium, and the distribution of the retroviral protein Gag at the plasma membrane.
Commentary: The original PALM paper by myself and my friend and co-inventor Harald Hess, spanning the before- and after-HHMI eras. Submitted and publicly presented months before other publications in the same year, the lessons of the paper remain widely misunderstood: 1) localization precision is not resolution; 2) the ability to resolve a few molecules by the Rayleigh criterion in a diffraction limited region (DLR) does not imply the ability to resolve structures of arbitrary complexity at the same scale; 3) true resolution well beyond the Abbe limit requires the ability to isolate and localize hundreds or thousands of molecules in one DLR; and 4) certain photoactivatable fluorescent proteins (PA-FPs) and caged dyes can be isolated and precisely localized at such densities; yielding true resolution down to 20 nm. The molecular densities we demonstrate (105 molecules/m2) are more than two orders of magnitude greater than in later papers that year (implying ten-fold better true resolution) – indeed, these papers demonstrate densities only comparable to earlier spectral or photobleaching based isolation methods. We validate our claims by correlative electron microscopy, and demonstrate the outstanding advantages of PA-FPs for superresolution microscopy: minimally perturbative sample preparation; high labeling densities; close binding to molecular targets; and zero non-specific background.
Fluorescence imaging of bulk-stained tissue is a popular technique for monitoring the activities in a large population of cells. However, a precise quantification of such experiments is often compromised by an ambiguity of background estimation. Although, in single-cell-staining experiments, background can be measured from a neighboring nonstained region, such a region often does not exist in bulk-stained tissue. Here we describe a novel method that overcomes this problem. In contrast to previous methods, we determined the background of a given region of interest (ROI) using the information contained in the temporal dynamics of its individual pixels. Since no information outside the ROI is needed, the method can be used regardless of the staining profile in the surrounding tissue. Moreover, we extend the method to deal with background inhomogeneities within a single ROI, a problem not yet solved by any of the currently available tools. We performed computer simulations to demonstrate the accuracy of our method and give example applications in ratiometric calcium imaging of bulk-stained olfactory bulb slices. Converting the fluorescence signals into [Ca2+] gives resting values consistent with earlier single-cell staining results, and odorant-induced [Ca2+] transients can be quantitatively compared in different cells. Using these examples we show that inaccurate background subtraction introduces large errors (easily in the range of 100%) in the assessment of both resting [Ca2+] and [Ca2+] dynamics. The proposed method allows us to avoid such errors.