Filter
Associated Lab
- Ahrens Lab (5) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (1) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (2) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (4) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Bock Lab (2) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (1) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Cui Lab (2) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (3) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (1) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (2) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (2) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (1) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (3) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (1) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (11) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (4) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (3) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (6) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (1) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (2) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (3) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (1) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (1) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (1) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keller Lab (10) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (4) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (3) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (11) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Looger Lab (10) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (3) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (3) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (3) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (1) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (2) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (5) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (1) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (5) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Satou Lab (2) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (3) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (7) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (1) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Singer Lab (9) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (2) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (6) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (3) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (10) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (1) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (3) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (2) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (2) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Wu Lab (3) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (2) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Publication Date
- December 2013 (13) Apply December 2013 filter
- November 2013 (10) Apply November 2013 filter
- October 2013 (20) Apply October 2013 filter
- September 2013 (19) Apply September 2013 filter
- August 2013 (15) Apply August 2013 filter
- July 2013 (19) Apply July 2013 filter
- June 2013 (17) Apply June 2013 filter
- May 2013 (10) Apply May 2013 filter
- April 2013 (12) Apply April 2013 filter
- March 2013 (11) Apply March 2013 filter
- February 2013 (19) Apply February 2013 filter
- January 2013 (29) Apply January 2013 filter
- Remove 2013 filter 2013
Type of Publication
194 Publications
Showing 121-130 of 194 resultsMany species are critically dependent on olfaction for survival. In the main olfactory system of mammals, odours are detected by sensory neurons that express a large repertoire of canonical odorant receptors and a much smaller repertoire of trace amine-associated receptors (TAARs). Odours are encoded in a combinatorial fashion across glomeruli in the main olfactory bulb, with each glomerulus corresponding to a specific receptor. The degree to which individual receptor genes contribute to odour perception is unclear. Here we show that genetic deletion of the olfactory Taar gene family, or even a single Taar gene (Taar4), eliminates the aversion that mice display to low concentrations of volatile amines and to the odour of predator urine. Our findings identify a role for the TAARs in olfaction, namely, in the high-sensitivity detection of innately aversive odours. In addition, our data reveal that aversive amines are represented in a non-redundant fashion, and that individual main olfactory receptor genes can contribute substantially to odour perception.
A basic task faced by the visual system of many organisms is to accurately track the position of moving prey. The retina is the first stage in the processing of such stimuli; the nature of the transformation here, from photons to spike trains, constrains not only the ultimate fidelity of the tracking signal but also the ease with which it can be extracted by other brain regions. Here we demonstrate that a population of fast-OFF ganglion cells in the salamander retina, whose dynamics are governed by a nonlinear circuit, serve to compute the future position of the target over hundreds of milliseconds. The extrapolated position of the target is not found by stimulus reconstruction but is instead computed by a weighted sum of ganglion cell outputs, the population vector average (PVA). The magnitude of PVA extrapolation varies systematically with target size, speed, and acceleration, such that large targets are tracked most accurately at high speeds, and small targets at low speeds, just as is seen in the motion of real prey. Tracking precision reaches the resolution of single photoreceptors, and the PVA algorithm performs more robustly than several alternative algorithms. If the salamander brain uses the fast-OFF cell circuit for target extrapolation as we suggest, the circuit dynamics should leave a microstructure on the behavior that may be measured in future experiments. Our analysis highlights the utility of simple computations that, while not globally optimal, are efficiently implemented and have close to optimal performance over a limited but ethologically relevant range of stimuli.
The histone variant H2A.Z is a genome-wide signature of nucleosomes proximal to eukaryotic regulatory DNA. Whereas the multisubunit chromatin remodeler SWR1 is known to catalyze ATP-dependent deposition of H2A.Z, the mechanism of SWR1 recruitment to S. cerevisiae promoters has been unclear. A sensitive assay for competitive binding of dinucleosome substrates revealed that SWR1 preferentially binds long nucleosome-free DNA and the adjoining nucleosome core particle, allowing discrimination of gene promoters over gene bodies. Analysis of mutants indicates that the conserved Swc2/YL1 subunit and the adenosine triphosphatase domain of Swr1 are mainly responsible for binding to substrate. SWR1 binding is enhanced on nucleosomes acetylated by the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase, but recognition of nucleosome-free and nucleosomal DNA is dominant over interaction with acetylated histones. Such hierarchical cooperation between DNA and histone signals expands the dynamic range of genetic switches, unifying classical gene regulation by DNA-binding factors with ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling and posttranslational histone modifications.
We demonstrate a meaningful prospective power analysis for an (admittedly idealized) illustrative connectome inference task. Modeling neurons as vertices and synapses as edges in a simple random graph model, we optimize the trade-off between the number of (putative) edges identified and the accuracy of the edge identification procedure. We conclude that explicit analysis of the quantity/quality trade-off is imperative for optimal neuroscientific experimental design. In particular, identifying edges faster/more cheaply, but with more error, can yield superior inferential performance.
Optogenetic tools can be used to manipulate neuronal activity in a reversible and specific manner. In recent years, such methods have been applied to uncover causal relationships between activity in specified neuronal circuits and behavior in the larval zebrafish. In this small, transparent, genetic model organism, noninvasive manipulation and monitoring of neuronal activity with light is possible throughout the nervous system. Here we review recent work in which these new tools have been applied to zebrafish, and discuss some of the existing challenges of these approaches.
Optogenetics combines optics and genetics to control neuronal activity with cell-type specificity and millisecond temporal precision. Its use in model organisms such as rodents, Drosophila, and Caenorhabditis elegans is now well-established. However, application of this technology in nonhuman primates (NHPs) has been slow to develop. One key challenge has been the delivery of viruses and light to the brain through the thick dura mater of NHPs, which can only be penetrated with large-diameter devices that damage the brain. The opacity of the NHP dura prevents visualization of the underlying cortex, limiting the spatial precision of virus injections, electrophysiological recordings, and photostimulation. Here, we describe a new optogenetics approach in which the native dura is replaced with an optically transparent artificial dura. This artificial dura can be penetrated with fine glass micropipettes, enabling precisely targeted injections of virus into brain tissue with minimal damage to cortex. The expression of optogenetic agents can be monitored visually over time. Most critically, this optical window permits targeted, noninvasive photostimulation and concomitant measurements of neuronal activity via intrinsic signal imaging and electrophysiological recordings. We present results from both anesthetized-paralyzed (optical imaging) and awake-behaving NHPs (electrophysiology). The improvements over current methods made possible by the artificial dura should enable the widespread use of optogenetic tools in NHP research, a key step toward the development of therapies for neuropsychiatric and neurological diseases in humans.
Determining how long-range synaptic inputs engage pyramidal neurons in primary motor cortex (M1) is important for understanding circuit mechanisms involved in regulating movement. We used channelrhodopsin-2-assisted circuit mapping to characterize the long-range excitatory synaptic connections made by multiple cortical and thalamic areas onto pyramidal neurons in mouse vibrissal motor cortex (vM1). Each projection innervated vM1 pyramidal neurons with a unique laminar profile. Collectively, the profiles for different sources of input partially overlapped and spanned all cortical layers. Specifically, orbital cortex (OC) inputs primarily targeted neurons in L6. Secondary motor cortex (M2) inputs excited neurons mainly in L5B, including pyramidal tract neurons. In contrast, thalamocortical inputs from anterior motor-related thalamic regions, including VA/VL (ventral anterior thalamic nucleus/ventrolateral thalamic nucleus), targeted neurons in L2/3 through L5B, but avoided L6. Inputs from posterior sensory-related thalamic areas, including POm (posterior thalamic nuclear group), targeted neurons only in the upper layers (L2/3 and L5A), similar to inputs from somatosensory (barrel) cortex. Our results show that long-range excitatory inputs target vM1 pyramidal neurons in a layer-specific manner. Inputs from sensory-related cortical and thalamic areas preferentially target the upper-layer pyramidal neurons in vM1. In contrast, inputs from OC and M2, areas associated with volitional and cognitive aspects of movements, bypass local circuitry and have direct monosynaptic access to neurons projecting to brainstem and thalamus.
Electron cryomicroscopy, or cryoEM, is an emerging technique for studying the three-dimensional structures of proteins and large macromolecular machines. Electron crystallography is a branch of cryoEM in which structures of proteins can be studied at resolutions that rival those achieved by X-ray crystallography. Electron crystallography employs two-dimensional crystals of a membrane protein embedded within a lipid bilayer. The key to a successful electron crystallographic experiment is the crystallization, or reconstitution, of the protein of interest. This unit describes ways in which protein can be expressed, purified, and reconstituted into well-ordered two-dimensional crystals. A protocol is also provided for negative stain electron microscopy as a tool for screening crystallization trials. When large and well-ordered crystals are obtained, the structures of both protein and its surrounding membrane can be determined to atomic resolution.
Different stimulus intensities elicit distinct perceptions, implying that input signals are either conveyed through an overlapping but distinct subpopulation of sensory neurons or channeled into divergent brain circuits according to intensity. In Drosophila, carbon dioxide (CO2) is detected by a single type of olfactory sensory neuron, but information is conveyed to higher brain centers through second-order projection neurons (PNs). Two distinct pathways, PN(v)-1 and PN(v)-2, are necessary and sufficient for avoidance responses to low and high CO2 concentrations, respectively. Whereas low concentrations activate PN(v)-1, high concentrations activate both PN(v)s and GABAergic PN(v)-3, which may inhibit PN(v)-1 pathway-mediated avoidance behavior. Channeling a sensory input into distinct neural pathways allows the perception of an odor to be further modulated by both stimulus intensity and context.
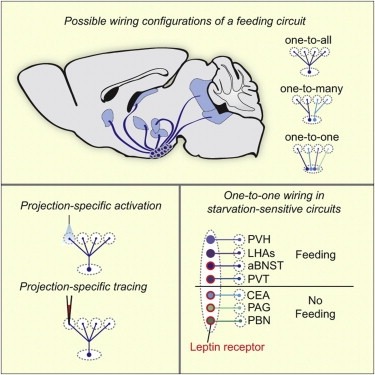
Neural circuits for essential natural behaviors are shaped by selective pressure to coordinate reliable execution of flexible goal-directed actions. However, the structural and functional organization of survival-oriented circuits is poorly understood due to exceptionally complex neuroanatomy. This is exemplified by AGRP neurons, which are a molecularly defined population that is sufficient to rapidly coordinate voracious food seeking and consumption behaviors. Here, we use cell-type-specific techniques for neural circuit manipulation and projection-specific anatomical analysis to examine the organization of this critical homeostatic circuit that regulates feeding. We show that AGRP neuronal circuits use a segregated, parallel, and redundant output configuration. AGRP neuron axon projections that target different brain regions originate from distinct subpopulations, several of which are sufficient to independently evoke feeding. The concerted anatomical and functional analysis of AGRP neuron projection populations reveals a constellation of core forebrain nodes, which are part of an extended circuit that mediates feeding behavior.