Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (16) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (64) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (40) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (38) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (113) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (13) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (17) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (53) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (42) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (64) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (13) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (15) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (12) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dennis Lab (1) Apply Dennis Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (46) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (25) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (50) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (11) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (19) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (7) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (41) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (29) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (38) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (91) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (62) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (63) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (94) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (27) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (77) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (2) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (46) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (6) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Kainmueller Lab (19) Apply Kainmueller Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (14) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (13) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (76) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (18) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (149) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (34) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (23) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (28) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (169) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (6) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (63) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (138) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (49) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (18) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (13) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (7) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (13) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (48) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (18) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (19) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (15) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (51) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (44) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (43) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (143) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (63) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (16) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (36) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (68) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (21) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (31) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (23) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (80) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (93) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (156) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (54) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (36) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (135) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (33) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (21) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (64) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (88) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (51) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (38) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (7) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (3) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (21) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (25) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wu Lab (9) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (28) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (25) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (12) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (3) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (11) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (53) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (49) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (46) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (4) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (18) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (26) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (49) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Publication Date
- 2025 (130) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (216) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (160) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (193) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (194) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (196) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (202) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (232) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (217) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (209) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (252) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (236) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (194) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (190) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (190) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (161) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (158) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (140) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (106) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (92) Apply 2006 filter
- 2005 (67) Apply 2005 filter
- 2004 (57) Apply 2004 filter
- 2003 (58) Apply 2003 filter
- 2002 (39) Apply 2002 filter
- 2001 (28) Apply 2001 filter
- 2000 (29) Apply 2000 filter
- 1999 (14) Apply 1999 filter
- 1998 (18) Apply 1998 filter
- 1997 (16) Apply 1997 filter
- 1996 (10) Apply 1996 filter
- 1995 (18) Apply 1995 filter
- 1994 (12) Apply 1994 filter
- 1993 (10) Apply 1993 filter
- 1992 (6) Apply 1992 filter
- 1991 (11) Apply 1991 filter
- 1990 (11) Apply 1990 filter
- 1989 (6) Apply 1989 filter
- 1988 (1) Apply 1988 filter
- 1987 (7) Apply 1987 filter
- 1986 (4) Apply 1986 filter
- 1985 (5) Apply 1985 filter
- 1984 (2) Apply 1984 filter
- 1983 (2) Apply 1983 filter
- 1982 (3) Apply 1982 filter
- 1981 (3) Apply 1981 filter
- 1980 (1) Apply 1980 filter
- 1979 (1) Apply 1979 filter
- 1976 (2) Apply 1976 filter
- 1973 (1) Apply 1973 filter
- 1970 (1) Apply 1970 filter
- 1967 (1) Apply 1967 filter
Type of Publication
4112 Publications
Showing 3721-3730 of 4112 resultsWe describe a scalable database cluster for the spatial analysis and annotation of high-throughput brain imaging data, initially for 3-d electron microscopy image stacks, but for time-series and multi-channel data as well. The system was designed primarily for workloads that build connectomes- neural connectivity maps of the brain-using the parallel execution of computer vision algorithms on high-performance compute clusters. These services and open-science data sets are publicly available at openconnecto.me. The system design inherits much from NoSQL scale-out and data-intensive computing architectures. We distribute data to cluster nodes by partitioning a spatial index. We direct I/O to different systems-reads to parallel disk arrays and writes to solid-state storage-to avoid I/O interference and maximize throughput. All programming interfaces are RESTful Web services, which are simple and stateless, improving scalability and usability. We include a performance evaluation of the production system, highlighting the effec-tiveness of spatial data organization.
The genome of the severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) contains eight open reading frames (ORFs) that encode novel proteins. These accessory proteins are dispensable for in vitro and in vivo replication and thus may be important for other aspects of virus-host interactions. We investigated the functions of the largest of the accessory proteins, the ORF 3a protein, using a 3a-deficient strain of SARS-CoV. Cell death of Vero cells after infection with SARS-CoV was reduced upon deletion of ORF 3a. Electron microscopy of infected cells revealed a role for ORF 3a in SARS-CoV induced vesicle formation, a prominent feature of cells from SARS patients. In addition, we report that ORF 3a is both necessary and sufficient for SARS-CoV-induced Golgi fragmentation and that the 3a protein accumulates and localizes to vesicles containing markers for late endosomes. Finally, overexpression of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (Arf1), a small GTPase essential for the maintenance of the Golgi apparatus, restored Golgi morphology during infection. These results establish an important role for ORF 3a in SARS-CoV-induced cell death, Golgi fragmentation, and the accumulation of intracellular vesicles.
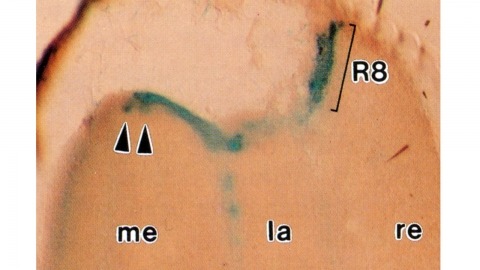
Histological staining of wild-type and sevenless transgenic Drosophila melanogaster bearing Rh3-lacZ fusion genes permits the selective visualization of polarization-sensitive R7 and R8 photoreceptor cells located along the dorsal anterior eye margin. Diffusion of beta-galactosidase throughout these cells reveals that they project long axons to the two most peripheral synaptic target rows of the dorsal posterior medulla, defining a specialized marginal zone of this optic lobe. Comparison of the staining patterns of marginal and nonmarginal Rh3-lacZ-expressing photoreceptor cells in the same histological preparations suggest that the marginal cells possess morphologically specialized axons and synaptic terminals. These findings are discussed with reference to the neuroanatomy of the corresponding dorsal marginal eye and optic lobe regions of the larger dipterans Musca and Calliphora, and in relation to the ability of Drosophila to orient to polarized light.
Parvalbumin and somatostatin inhibitory interneurons gate information flow in discrete cortical areas that compute sensory and cognitive functions. Despite the considerable differences between areas, individual interneuron subtypes are genetically invariant and are thought to form canonical circuits regardless of which area they are embedded in. Here, we investigate whether this is achieved through selective and systematic variations in their afferent connectivity during development. To this end, we examined the development of their inputs within distinct cortical areas. We find that interneuron afferents show little evidence of being globally stereotyped. Rather, each subtype displays characteristic regional connectivity and distinct developmental dynamics by which this connectivity is achieved. Moreover, afferents dynamically regulated during development are disrupted by early sensory deprivation and in a model of fragile X syndrome. These data provide a comprehensive map of interneuron afferents across cortical areas and reveal the logic by which these circuits are established during development.
Visual pathways from the compound eye of an insect relay to four neuropils, successively the lamina, medulla, lobula, and lobula plate in the underlying optic lobe. Among these neuropils, the medulla, lobula, and lobula plate are interconnected by the complex second optic chiasm, through which the anteroposterior axis undergoes an inversion between the medulla and lobula. Given their complex structure, the projection patterns through the second optic chiasm have so far lacked critical analysis. By densely reconstructing axon trajectories using a volumetric scanning electron microscopy (SEM) technique, we reveal the three-dimensional structure of the second optic chiasm of , which comprises interleaving bundles and sheets of axons insulated from each other by glial sheaths. These axon bundles invert their horizontal sequence in passing between the medulla and lobula. Axons connecting the medulla and lobula plate are also bundled together with them but do not decussate the sequence of their horizontal positions. They interleave with sheets of projection neuron axons between the lobula and lobula plate, which also lack decussations. We estimate that approximately 19,500 cells per hemisphere, about two thirds of the optic lobe neurons, contribute to the second chiasm, most being Tm cells, with an estimated additional 2,780 T4 and T5 cells each. The chiasm mostly comprises axons and cell body fibers, but also a few synaptic elements. Based on our anatomical findings, we propose that a chiasmal structure between the neuropils is potentially advantageous for processing complex visual information in parallel. The EM reconstruction shows not only the structure of the chiasm in the adult brain, the previously unreported main topic of our study, but also suggest that the projection patterns of the neurons comprising the chiasm may be determined by the proliferation centers from which the neurons develop. Such a complex wiring pattern could, we suggest, only have arisen in several evolutionary steps.
Mutualisms are mutually beneficial interactions between species and are fundamentally important at all levels of biological organization. It is not clear, however, why one species participates in a particular mutualism whereas another does not. Here we show that pre-existing traits can dispose particular species to evolve a mutualistic interaction. Combining morphological, ecological, and behavioral data in a comparative analysis, we show that resource use in Chaitophorus aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) modulates the origin of their mutualism with ants. We demonstrate that aphid species that feed on deeper phloem elements have longer mouthparts, that this inhibits their ability to withdraw their mouthparts and escape predators and that, consequently, this increases their need for protection by mutualist ants.
Insect metamorphosis is a fascinating and highly successful biological adaptation, but there is much uncertainty as to how it evolved. Ancestral insect species did not undergo metamorphosis and there are still some existing species that lack metamorphosis or undergo only partial metamorphosis. Based on endocrine studies and morphological comparisons of the development of insect species with and without metamorphosis, a novel hypothesis for the evolution of metamorphosis is proposed. Changes in the endocrinology of development are central to this hypothesis. The three stages of the ancestral insect species-pronymph, nymph and adult-are proposed to be equivalent to the larva, pupa and adult stages of insects with complete metamorphosis. This proposal has general implications for insect developmental biology.
Transmembrane transporter proteins allow the passage of essentially all biologically important molecules across the lipid membranes of cells and organelles and are therefore of central importance to all forms of life. Current methods of transporter measurement, however, are lacking in several dimensions. Herein, a method is presented in which oscillating stimuli are presented to transporter-expressing cells, and activity is measured through imaging the corresponding oscillating responses of intracellular fluorescent sensors. This approach yields continuous temporal readouts of transporter activity and can therefore be used to measure time-dependent responses to drugs and other stimuli. Because of the periodic nature of the response, temporal Fourier transforms can be used to identify and quantify regions of interest in the xy plane and to overcome noise. This technique, called the Oscillating Stimulus Transporter Assay (OSTA), should greatly facilitate both functional characterization of transporters as well as high-throughput screening of drugs for transporters of particular pathophysiological interest.
Protein-protein interactions are challenging targets for modulation by small molecules. Here, we propose an approach that harnesses the increasing structural coverage of protein complexes to identify small molecules that may target protein interactions. Specifically, we identify ligand and protein binding sites that overlap upon alignment of homologous proteins. Of the 2,619 protein structure families observed to bind proteins, 1,028 also bind small molecules (250-1000 Da), and 197 exhibit a statistically significant (p<0.01) overlap between ligand and protein binding positions. These "bi-functional positions", which bind both ligands and proteins, are particularly enriched in tyrosine and tryptophan residues, similar to "energetic hotspots" described previously, and are significantly less conserved than mono-functional and solvent exposed positions. Homology transfer identifies ligands whose binding sites overlap at least 20% of the protein interface for 35% of domain-domain and 45% of domain-peptide mediated interactions. The analysis recovered known small-molecule modulators of protein interactions as well as predicted new interaction targets based on the sequence similarity of ligand binding sites. We illustrate the predictive utility of the method by suggesting structural mechanisms for the effects of sanglifehrin A on HIV virion production, bepridil on the cellular entry of anthrax edema factor, and fusicoccin on vertebrate developmental pathways. The results, available at http://pibase.janelia.org, represent a comprehensive collection of structurally characterized modulators of protein interactions, and suggest that homologous structures are a useful resource for the rational design of interaction modulators.
The macronuclear genome of the ciliate Oxytricha trifallax displays an extreme and unique eukaryotic genome architecture with extensive genomic variation. During sexual genome development, the expressed, somatic macronuclear genome is whittled down to the genic portion of a small fraction (\~{}5%) of its precursor "silent" germline micronuclear genome by a process of "unscrambling" and fragmentation. The tiny macronuclear "nanochromosomes" typically encode single, protein-coding genes (a small portion, 10%, encode 2-8 genes), have minimal noncoding regions, and are differentially amplified to an average of \~{}2,000 copies. We report the high-quality genome assembly of \~{}16,000 complete nanochromosomes (\~{}50 Mb haploid genome size) that vary from 469 bp to 66 kb long (mean \~{}3.2 kb) and encode \~{}18,500 genes. Alternative DNA fragmentation processes \~{}10% of the nanochromosomes into multiple isoforms that usually encode complete genes. Nucleotide diversity in the macronucleus is very high (SNP heterozygosity is \~{}4.0%), suggesting that Oxytricha trifallax may have one of the largest known effective population sizes of eukaryotes. Comparison to other ciliates with nonscrambled genomes and long macronuclear chromosomes (on the order of 100 kb) suggests several candidate proteins that could be involved in genome rearrangement, including domesticated MULE and IS1595-like DDE transposases. The assembly of the highly fragmented Oxytricha macronuclear genome is the first completed genome with such an unusual architecture. This genome sequence provides tantalizing glimpses into novel molecular biology and evolution. For example, Oxytricha maintains tens of millions of telomeres per cell and has also evolved an intriguing expansion of telomere end-binding proteins. In conjunction with the micronuclear genome in progress, the O. trifallax macronuclear genome will provide an invaluable resource for investigating programmed genome rearrangements, complementing studies of rearrangements arising during evolution and disease.