Filter
Associated Lab
- Ahrens Lab (4) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (1) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (1) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (1) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Harris Lab (4) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (1) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (9) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (1) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keller Lab (1) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (8) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (1) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (1) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (24) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (5) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (1) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Remove Schreiter Lab filter Schreiter Lab
- Stringer Lab (1) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (13) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (1) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Turner Lab (4) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (1) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Associated Support Team
- Anatomy and Histology (2) Apply Anatomy and Histology filter
- Janelia Experimental Technology (4) Apply Janelia Experimental Technology filter
- Molecular Genomics (5) Apply Molecular Genomics filter
- Primary & iPS Cell Culture (5) Apply Primary & iPS Cell Culture filter
- Project Technical Resources (1) Apply Project Technical Resources filter
- Viral Tools (4) Apply Viral Tools filter
Publication Date
- 2025 (3) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (5) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (6) Apply 2023 filter
- 2021 (1) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (5) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (4) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (4) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (4) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (2) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (4) Apply 2015 filter
- 2013 (5) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (2) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (2) Apply 2011 filter
- 2009 (2) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (1) Apply 2008 filter
50 Janelia Publications
Showing 31-40 of 50 resultsCalcium imaging with genetically encoded calcium indicators (GECIs) is routinely used to measure neural activity in intact nervous systems. GECIs are frequently used in one of two different modes: to track activity in large populations of neuronal cell bodies, or to follow dynamics in subcellular compartments such as axons, dendrites and individual synaptic compartments. Despite major advances, calcium imaging is still limited by the biophysical properties of existing GECIs, including affinity, signal-to-noise ratio, rise and decay kinetics, and dynamic range. Using structure-guided mutagenesis and neuron-based screening, we optimized the green fluorescent protein-based GECI GCaMP6 for different modes of in vivo imaging. The jGCaMP7 sensors provide improved detection of individual spikes (jGCaMP7s,f), imaging in neurites and neuropil (jGCaMP7b), and tracking large populations of neurons using 2-photon (jGCaMP7s,f) or wide-field (jGCaMP7c) imaging.
Genetically encoded calcium indicators (GECIs) can be used to image activity in defined neuronal populations. However, current GECIs produce inferior signals compared to synthetic indicators and recording electrodes, precluding detection of low firing rates. We developed a single-wavelength GCaMP2-based GECI (GCaMP3), with increased baseline fluorescence (3-fold), increased dynamic range (3-fold) and higher affinity for calcium (1.3-fold). We detected GCaMP3 fluorescence changes triggered by single action potentials in pyramidal cell dendrites, with signal-to-noise ratio and photostability substantially better than those of GCaMP2, D3cpVenus and TN-XXL. In Caenorhabditis elegans chemosensory neurons and the Drosophila melanogaster antennal lobe, sensory stimulation-evoked fluorescence responses were significantly enhanced with GCaMP3 (4-6-fold). In somatosensory and motor cortical neurons in the intact mouse, GCaMP3 detected calcium transients with amplitudes linearly dependent on action potential number. Long-term imaging in the motor cortex of behaving mice revealed large fluorescence changes in imaged neurons over months.
Marking functionally distinct neuronal ensembles with high spatiotemporal resolution is a key challenge in systems neuroscience. We recently introduced CaMPARI, an engineered fluorescent protein whose green-to-red photoconversion depends on simultaneous light exposure and elevated calcium, which enabled marking active neuronal populations with single-cell and subsecond resolution. However, CaMPARI (CaMPARI1) has several drawbacks, including background photoconversion in low calcium, slow kinetics and reduced fluorescence after chemical fixation. In this work, we develop CaMPARI2, an improved sensor with brighter green and red fluorescence, faster calcium unbinding kinetics and decreased photoconversion in low calcium conditions. We demonstrate the improved performance of CaMPARI2 in mammalian neurons and in vivo in larval zebrafish brain and mouse visual cortex. Additionally, we herein develop an immunohistochemical detection method for specific labeling of the photoconverted red form of CaMPARI. The anti-CaMPARI-red antibody provides strong labeling that is selective for photoconverted CaMPARI in activated neurons in rodent brain tissue.
Neurochemical signals like dopamine (DA) play a crucial role in a variety of brain functions through intricate interactions with other neuromodulators and intracellular signaling pathways. However, studying these complex networks has been hindered by the challenge of detecting multiple neurochemicals in vivo simultaneously. To overcome this limitation, we developed a single-protein chemigenetic DA sensor, HaloDA1.0, which combines a cpHaloTag-chemical dye approach with the G protein-coupled receptor activation-based (GRAB) strategy, providing high sensitivity for DA, sub-second response kinetics, and an extensive spectral range from far-red to near-infrared. When used together with existing green and red fluorescent neuromodulator sensors, Ca2+ indicators, cAMP sensors, and optogenetic tools, HaloDA1.0 provides high versatility for multiplex imaging in cultured neurons, brain slices, and behaving animals, facilitating in-depth studies of dynamic neurochemical networks.
We have developed a series of yellow genetically encoded Ca indicators for optical imaging (Y-GECOs) with inverted responses to Ca and apparent dissociation constants (K') ranging from 25 to 2400 nM. To demonstrate the utility of this affinity series of Ca indicators, we expressed the four highest affinity variants (K's = 25, 63, 121, and 190 nM) in the Drosophila medulla intrinsic neuron Mi1. Hyperpolarization of Mi1 by optogenetic stimulation of the laminar monopolar neuron L1 produced a decrease in intracellular Ca in layers 8-10, and a corresponding increase in Y-GECO fluorescence. These experiments revealed that lower K' was associated with greater increases in fluorescence, but longer delays to reach the maximum signal change due to slower off-rate kinetics.
Femtosecond lasers at fixed wavelengths above 1,000 nm are powerful, stable and inexpensive, making them promising sources for two-photon microscopy. Biosensors optimized for these wavelengths are needed for both next-generation microscopes and affordable turn-key systems. Here we report jYCaMP1, a yellow variant of the calcium indicator jGCaMP7 that outperforms its parent in mice and flies at excitation wavelengths above 1,000 nm and enables improved two-color calcium imaging with red fluorescent protein-based indicators.
Point-scanning two-photon microscopy enables high-resolution imaging within scattering specimens such as the mammalian brain, but sequential acquisition of voxels fundamentally limits imaging speed. We developed a two-photon imaging technique that scans lines of excitation across a focal plane at multiple angles and uses prior information to recover high-resolution images at over 1.4 billion voxels per second. Using a structural image as a prior for recording neural activity, we imaged visually-evoked and spontaneous glutamate release across hundreds of dendritic spines in mice at depths over 250 microns and frame-rates over 1 kHz. Dendritic glutamate transients in anaesthetized mice are synchronized within spatially-contiguous domains spanning tens of microns at frequencies ranging from 1-100 Hz. We demonstrate high-speed recording of acetylcholine and calcium sensors, 3D single-particle tracking, and imaging in densely-labeled cortex. Our method surpasses limits on the speed of raster-scanned imaging imposed by fluorescence lifetime.
The identification of active neurons and circuits in vivo is a fundamental challenge in understanding the neural basis of behavior. Genetically encoded calcium (Ca(2+)) indicators (GECIs) enable quantitative monitoring of cellular-resolution activity during behavior. However, such indicators require online monitoring within a limited field of view. Alternatively, post hoc staining of immediate early genes (IEGs) indicates highly active cells within the entire brain, albeit with poor temporal resolution. We designed a fluorescent sensor, CaMPARI, that combines the genetic targetability and quantitative link to neural activity of GECIs with the permanent, large-scale labeling of IEGs, allowing a temporally precise "activity snapshot" of a large tissue volume. CaMPARI undergoes efficient and irreversible green-to-red conversion only when elevated intracellular Ca(2+) and experimenter-controlled illumination coincide. We demonstrate the utility of CaMPARI in freely moving larvae of zebrafish and flies, and in head-fixed mice and adult flies.
Genetically encoded calcium indicators (GECIs), together with modern microscopy, allow repeated activity measurement, in real time and with cellular resolution, of defined cellular populations. Recent efforts in protein engineering have yielded several high-quality GECIs that facilitate new applications in neuroscience. Here, we summarize recent progress in GECI design, optimization, and characterization, and provide guidelines for selecting the appropriate GECI for a given biological application. We focus on the unique challenges associated with imaging in behaving animals.
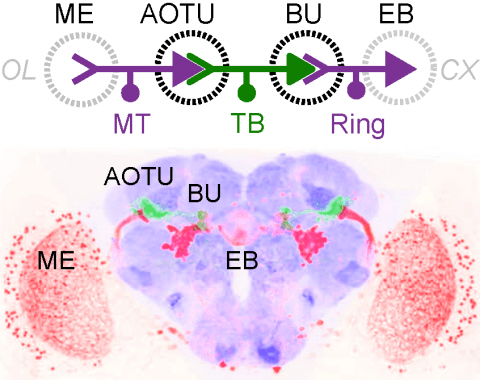
Many animals orient using visual cues, but how a single cue is selected from among many is poorly understood. Here we show that Drosophila ring neurons—central brain neurons implicated in navigation—display visual stimulus selection. Using in vivo two-color two-photon imaging with genetically encoded calcium indicators, we demonstrate that individual ring neurons inherit simple-cell-like receptive fields from their upstream partners. Stimuli in the contralateral visual field suppressed responses to ipsilateral stimuli in both populations. Suppression strength depended on when and where the contralateral stimulus was presented, an effect stronger in ring neurons than in their upstream inputs. This history-dependent effect on the temporal structure of visual responses, which was well modeled by a simple biphasic filter, may determine how visual references are selected for the fly's internal compass. Our approach highlights how two-color calcium imaging can help identify and localize the origins of sensory transformations across synaptically connected neural populations.