Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (1) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (53) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (40) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (19) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (101) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (8) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (14) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (50) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (36) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (45) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (10) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (14) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (8) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (32) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (21) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (38) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (4) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (15) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (7) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (31) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (16) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (38) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (59) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (34) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (53) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (13) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (23) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (74) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (2) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (42) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (1) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (13) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (8) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (61) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (2) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (137) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (29) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (19) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (4) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (97) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (1) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (58) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (137) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (31) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (12) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (6) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (6) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (1) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (36) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (5) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (7) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (4) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (45) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (20) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (31) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (105) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (46) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (1) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (36) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (50) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (1) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (31) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (18) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (37) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (57) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (73) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (47) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (32) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (131) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (9) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (18) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (17) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (58) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (39) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (27) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (7) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (3) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (21) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (6) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wu Lab (8) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (26) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (5) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (12) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (3) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (11) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (53) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (49) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (46) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (4) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (18) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (26) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (45) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Associated Support Team
- Project Pipeline Support (5) Apply Project Pipeline Support filter
- Anatomy and Histology (18) Apply Anatomy and Histology filter
- Cryo-Electron Microscopy (36) Apply Cryo-Electron Microscopy filter
- Electron Microscopy (16) Apply Electron Microscopy filter
- Gene Targeting and Transgenics (11) Apply Gene Targeting and Transgenics filter
- Integrative Imaging (17) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Invertebrate Shared Resource (40) Apply Invertebrate Shared Resource filter
- Janelia Experimental Technology (37) Apply Janelia Experimental Technology filter
- Management Team (1) Apply Management Team filter
- Molecular Genomics (15) Apply Molecular Genomics filter
- Primary & iPS Cell Culture (14) Apply Primary & iPS Cell Culture filter
- Project Technical Resources (50) Apply Project Technical Resources filter
- Quantitative Genomics (19) Apply Quantitative Genomics filter
- Scientific Computing Software (92) Apply Scientific Computing Software filter
- Scientific Computing Systems (7) Apply Scientific Computing Systems filter
- Viral Tools (14) Apply Viral Tools filter
- Vivarium (7) Apply Vivarium filter
Publication Date
- 2025 (126) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (215) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (159) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (167) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (175) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (177) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (177) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (206) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (186) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (191) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (195) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (190) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (136) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (112) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (98) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (61) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (56) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (40) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (21) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (3) Apply 2006 filter
2691 Janelia Publications
Showing 1671-1680 of 2691 resultsLocomotor systems generate diverse motor patterns to produce the movements underlying behavior, requiring that motor neurons be recruited at various phases of the locomotor cycle. Reciprocal inhibition produces alternating motor patterns; however, the mechanisms that generate other phasic relationships between intrasegmental motor pools are unknown. Here, we investigate one such motor pattern in the Drosophila larva, using a multidisciplinary approach including electrophysiology and ssTEM-based circuit reconstruction. We find that two motor pools that are sequentially recruited during locomotion have identical excitable properties. In contrast, they receive input from divergent premotor circuits. We find that this motor pattern is not orchestrated by differential excitatory input but by a GABAergic interneuron acting as a delay line to the later-recruited motor pool. Our findings show how a motor pattern is generated as a function of the modular organization of locomotor networks through segregation of inhibition, a potentially general mechanism for sequential motor patterns.
Efficient hydrolysis of amide bonds has long been a reaction of interest for organic chemists. The rate constants of proteases are unmatched by those of any synthetic catalyst. It has been proposed that a dipeptide containing serine and histidine is an effective catalyst of amide hydrolysis, based on an apparent ability to degrade a protein. The capacity of the Ser-His dipeptide to catalyze the hydrolysis of several discrete ester and amide substrates is investigated using previously described conditions. This dipeptide does not catalyze the hydrolysis of amide or unactivated ester groups in any of the substrates under the conditions evaluated.
Myelin is best known for its role in increasing the conduction velocity and metabolic efficiency of long-range excitatory axons. Accordingly, the myelin observed in neocortical gray matter is thought to mostly ensheath excitatory axons connecting to subcortical regions and distant cortical areas. Using independent analyses of light and electron microscopy data from mouse neocortex, we show that a surprisingly large fraction of cortical myelin (half the myelin in layer 2/3 and a quarter in layer 4) ensheathes axons of inhibitory neurons, specifically of parvalbumin-positive basket cells. This myelin differs significantly from that of excitatory axons in distribution and protein composition. Myelin on inhibitory axons is unlikely to meaningfully hasten the arrival of spikes at their pre-synaptic terminals, due to the patchy distribution and short path-lengths observed. Our results thus highlight the need for exploring alternative roles for myelin in neocortical circuits.
Destabilized nanobodies can be used to deliver fluorescent proteins and enzymes to specific targets inside cells.
A 60-year-old man diagnosed with macular telangiectasia type 1 (MacTel 1) was treated for 3 years with monthly aflibercept (Eylea; Regeneron, Tarrytown, NY) and serially imaged with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. When administered monthly, aflibercept appeared to have a beneficial effect on macular edema secondary to MacTel 1. Visual acuity preservation despite minimal chronic macular edema could be attributed to the lack of significant photoreceptor disruption.
It is unclear how regulatory genes establish neural circuits that compose sex-specific behaviors. The Drosophila melanogaster male courtship song provides a powerful model to study this problem. Courting males vibrate a wing to sing bouts of pulses and hums, called pulse and sine song, respectively. We report the discovery of male-specific thoracic interneurons—the TN1A neurons—that are required specifically for sine song. The TN1A neurons can drive the activity of a sex-non-specific wing motoneuron, hg1, which is also required for sine song. The male-specific connection between the TN1A neurons and the hg1 motoneuron is regulated by the sexual differentiation gene doublesex. We find that doublesex is required in the TN1A neurons during development to increase the density of the TN1A arbors that interact with dendrites of the hg1motoneuron. Our findings demonstrate how a sexual differentiation gene can build a sex-specific circuit motif by modulating neuronal arborization. •Doublesex-expressing TN1 neurons are necessary and sufficient for the male sine song•A subclass of TN1 neurons, TN1A, contributes to the sine song•TN1A neurons are functionally coupled to a sine song motoneuron, hg1•Doublesex regulates the connectivity between the TN1A and hg1 neurons It is unclear how developmental regulatory genes specify sex-specific behaviors. Shirangi et al. demonstrate that the Drosophila sexual differentiation gene doublesex encodes a sex-specific behavior—male song—by promoting the connectivity between the male-specific TN1A neurons and the sex-non-specific hg1 neurons, which are required for production of the song.
Electrical coupling in circuits can produce non-intuitive circuit dynamics, as seen in both experimental work from the crustacean stomatogastric ganglion and in computational models inspired by the connectivity in this preparation. Ambiguities in interpreting the results of electrophysiological recordings can arise if sets of pre- or postsynaptic neurons are electrically coupled, or if the electrical coupling exhibits some specificity (e.g. rectifying, or voltage-dependent). Even in small circuits, electrical coupling can produce parallel pathways that can allow information to travel by monosynaptic and/or polysynaptic pathways. Consequently, similar changes in circuit dynamics can arise from entirely different underlying mechanisms. When neurons are coupled both chemically and electrically, modifying the relative strengths of the two interactions provides a mechanism for flexibility in circuit outputs. This, together with neuromodulation of gap junctions and coupled neurons is important both in developing and adult circuits. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Microelectron diffraction (MicroED) is a new cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) method capable of determining macromolecular structures at atomic resolution from vanishingly small 3D crystals. MicroED promises to solve atomic resolution structures from even the tiniest of crystals, less than a few hundred nanometers thick. MicroED complements frontier advances in crystallography and represents part of the rebirth of cryo-EM that is making macromolecular structure determination more accessible for all. Here we review the concept and practice of MicroED, for both the electron microscopist and crystallographer. Where other reviews have addressed specific details of the technique (Hattne et al., 2015, Shi et al., 2016 and Shi et al., 2013), we aim to provide context and highlight important features that should be considered when performing a MicroED experiment.
Following considerable progress on the molecular and cellular basis of taste perception in fly sensory neurons, the time is now ripe to explore how taste information, integrated with hunger and satiety, undergo a sensorimotor transformation to lead to the motor actions of feeding behavior. I examine what is known of feeding circuitry in adult flies from more than 250 years of work in larger flies and from newer work in Drosophila. I review the anatomy of the proboscis, its muscles and their functions (where known), its motor neurons, interneurons known to receive taste inputs, interneurons that diverge from taste circuitry to provide information to other circuits, interneurons from other circuits that converge on feeding circuits, proprioceptors that influence the motor control of feeding, and sites of integration of hunger and satiety on feeding circuits. In spite of the several neuron types now known, a connected pathway from taste inputs to feeding motor outputs has yet to be found. We are on the threshold of an era where these individual components will be assembled into circuits, revealing how nervous system architecture leads to the control of behavior.
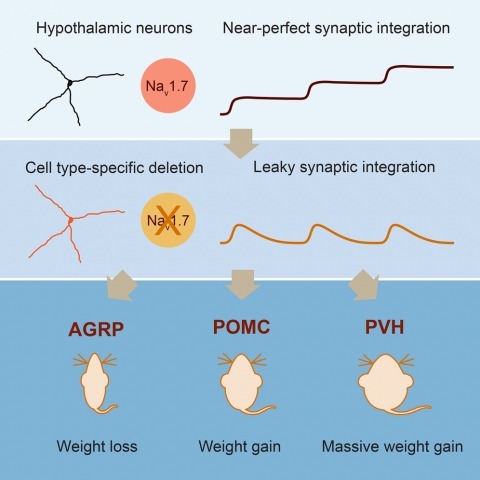
Neurons are well suited for computations on millisecond timescales, but some neuronal circuits set behavioral states over long time periods, such as those involved in energy homeostasis. We found that multiple types of hypothalamic neurons, including those that oppositely regulate body weight, are specialized as near-perfect synaptic integrators that summate inputs over extended timescales. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are greatly prolonged, outlasting the neuronal membrane time-constant up to 10-fold. This is due to the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 (Scn9a), previously associated with pain-sensation but not synaptic integration. Scn9a deletion in AGRP, POMC, or paraventricular hypothalamic neurons reduced EPSP duration, synaptic integration, and altered body weight in mice. In vivo whole-cell recordings in the hypothalamus confirmed near-perfect synaptic integration. These experiments show that integration of synaptic inputs over time by Nav1.7 is critical for body weight regulation and reveal a mechanism for synaptic control of circuits regulating long term homeostatic functions.