Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (16) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (64) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (40) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (38) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (113) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (13) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (17) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (53) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (42) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (64) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (13) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (15) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (12) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dennis Lab (1) Apply Dennis Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (46) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (25) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (50) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (11) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (19) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (7) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (41) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (29) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (38) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (91) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (62) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (63) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (94) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (27) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (77) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (2) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (46) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (6) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Kainmueller Lab (19) Apply Kainmueller Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (14) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (13) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (76) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (18) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (149) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (34) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (23) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (28) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (169) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (6) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (63) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (138) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (49) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (18) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (13) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (7) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (13) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (48) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (18) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (19) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (15) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (51) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (44) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (43) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (143) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (63) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (16) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (36) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (67) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (21) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (31) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (23) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (80) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (93) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (156) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (54) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (35) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (135) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (33) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (21) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (64) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (88) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (51) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (38) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (7) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (3) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (21) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (25) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wu Lab (9) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (28) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (25) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (12) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (3) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (11) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (53) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (49) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (46) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (4) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (18) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (26) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (49) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Publication Date
- 2025 (126) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (216) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (160) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (193) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (194) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (196) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (202) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (232) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (217) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (209) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (252) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (236) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (194) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (190) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (190) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (161) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (158) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (140) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (106) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (92) Apply 2006 filter
- 2005 (67) Apply 2005 filter
- 2004 (57) Apply 2004 filter
- 2003 (58) Apply 2003 filter
- 2002 (39) Apply 2002 filter
- 2001 (28) Apply 2001 filter
- 2000 (29) Apply 2000 filter
- 1999 (14) Apply 1999 filter
- 1998 (18) Apply 1998 filter
- 1997 (16) Apply 1997 filter
- 1996 (10) Apply 1996 filter
- 1995 (18) Apply 1995 filter
- 1994 (12) Apply 1994 filter
- 1993 (10) Apply 1993 filter
- 1992 (6) Apply 1992 filter
- 1991 (11) Apply 1991 filter
- 1990 (11) Apply 1990 filter
- 1989 (6) Apply 1989 filter
- 1988 (1) Apply 1988 filter
- 1987 (7) Apply 1987 filter
- 1986 (4) Apply 1986 filter
- 1985 (5) Apply 1985 filter
- 1984 (2) Apply 1984 filter
- 1983 (2) Apply 1983 filter
- 1982 (3) Apply 1982 filter
- 1981 (3) Apply 1981 filter
- 1980 (1) Apply 1980 filter
- 1979 (1) Apply 1979 filter
- 1976 (2) Apply 1976 filter
- 1973 (1) Apply 1973 filter
- 1970 (1) Apply 1970 filter
- 1967 (1) Apply 1967 filter
Type of Publication
4108 Publications
Showing 1061-1070 of 4108 resultsNatural physical, chemical, and biological dynamical systems are often complex, with heterogeneous components interacting in diverse ways. We show that graph neural networks can be designed to jointly learn the interaction rules and the structure of the heterogeneity from data alone. The learned latent structure and dynamics can be used to virtually decompose the complex system which is necessary to parameterize and infer the underlying governing equations. We tested the approach with simulation experiments of moving particles and vector fields that interact with each other. While our current aim is to better understand and validate the approach with simulated data, we anticipate it to become a generally applicable tool to uncover the governing rules underlying complex dynamics observed in nature.
Behavior has molecular, cellular, and circuit determinants. However, because many proteins are broadly expressed, their acute manipulation within defined cells has been difficult. Here, we combined the speed and molecular specificity of pharmacology with the cell type specificity of genetic tools. DART (drugs acutely restricted by tethering) is a technique that rapidly localizes drugs to the surface of defined cells, without prior modification of the native target. We first developed an AMPAR antagonist DART, with validation in cultured neuronal assays, in slices of mouse dorsal striatum, and in behaving mice. In parkinsonian animals, motor deficits were causally attributed to AMPARs in indirect spiny projection neurons (iSPNs) and to excess phasic firing of tonically active interneurons (TANs). Together, iSPNs and TANs (i.e., D2 cells) drove akinesia, whereas movement execution deficits reflected the ratio of AMPARs in D2 versus D1 cells. Finally, we designed a muscarinic antagonist DART in one iteration, demonstrating applicability of the method to diverse targets.
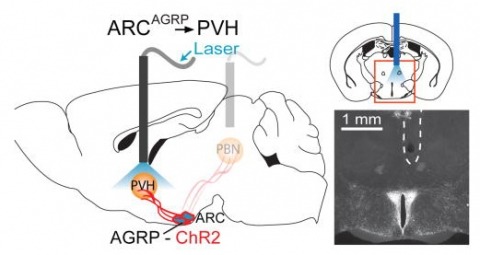
Hunger is a complex behavioural state that elicits intense food seeking and consumption. These behaviours are rapidly recapitulated by activation of starvation-sensitive AGRP neurons, which present an entry point for reverse-engineering neural circuits for hunger. Here we mapped synaptic interactions of AGRP neurons with multiple cell populations in mice and probed the contribution of these distinct circuits to feeding behaviour using optogenetic and pharmacogenetic techniques. An inhibitory circuit with paraventricular hypothalamus (PVH) neurons substantially accounted for acute AGRP neuron-evoked eating, whereas two other prominent circuits were insufficient. Within the PVH, we found that AGRP neurons target and inhibit oxytocin neurons, a small population that is selectively lost in Prader-Willi syndrome, a condition involving insatiable hunger. By developing strategies for evaluating molecularly defined circuits, we show that AGRP neuron suppression of oxytocin neurons is critical for evoked feeding. These experiments reveal a new neural circuit that regulates hunger state and pathways associated with overeating disorders.
Serine hydrolases have diverse intracellular substrates, biological functions, and structural plasticity, and are thus important for biocatalyst design. Amongst serine hydrolases, the recently described ybfF enzyme family are promising novel biocatalysts with an unusual bifurcated substrate-binding cleft and the ability to recognize commercially relevant substrates. We characterized in detail the substrate selectivity of a novel ybfF enzyme from Vibrio cholerae (Vc-ybfF) by using a 21-member library of fluorogenic ester substrates. We assigned the roles of the two substrate-binding clefts in controlling the substrate selectivity and folded stability of Vc-ybfF by comprehensive substitution analysis. The overall substrate preference of Vc-ybfF was for short polar chains, but it retained significant activity with a range of cyclic and extended esters. This broad substrate specificity combined with the substitutional analysis demonstrates that the larger binding cleft controls the substrate specificity of Vc-ybfF. Key selectivity residues (Tyr116, Arg120, Tyr209) are also located at the larger binding pocket and control the substrate specificity profile. In the structure of ybfF the narrower binding cleft contains water molecules prepositioned for hydrolysis, but based on substitution this cleft showed only minimal contribution to catalysis. Instead, the residues surrounding the narrow binding cleft and at the entrance to the binding pocket contributed significantly to the folded stability of Vc-ybfF. The relative contributions of each cleft of the binding pocket to the catalytic activity and folded stability of Vc-ybfF provide a valuable map for designing future biocatalysts based on the ybfF scaffold.
Young birds learn to sing by using auditory feedback to compare their own vocalizations to a memorized or innate song pattern; if they are deafened as juveniles, they will not develop normal songs. The completion of song development is called crystallization. After this stage, song shows little variation in its temporal or spectral properties. However, the mechanisms underlying this stability are largely unknown. Here we present evidence that auditory feedback is actively used in adulthood to maintain the stability of song structure. We found that perturbing auditory feedback during singing in adult zebra finches caused their song to deteriorate slowly. This ’decrystallization’ consisted of a marked loss of the spectral and temporal stereotypy seen in crystallized song, including stuttering, creation, deletion and distortion of song syllables. After normal feedback was restored, these deviations gradually disappeared and the original song was recovered. Thus, adult birds that do not learn new songs nevertheless retain a significant amount of plasticity in the brain.
To integrate changing environmental cues with high spatial and temporal resolution is critical for animals to orient themselves. Drosophila larvae show an effective motor program to navigate away from light sources. How the larval visual circuit processes light stimuli to control navigational decision remains unknown. The larval visual system is composed of two sensory input channels, Rhodopsin5 (Rh5) and Rhodopsin6 (Rh6) expressing photoreceptors (PRs). We here characterize how spatial and temporal information are used to control navigation. Rh6-PRs are required to perceive temporal changes of light intensity during head casts, while Rh5-PRs are required to control behaviors that allow navigation in response to spatial cues. We characterize how distinct behaviors are modulated and identify parallel acting and converging features of the visual circuit. Functional features of the larval visual circuit highlight the principle of how early in a sensory circuit distinct behaviors may be computed by partly overlapping sensory pathways.
Single-molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) has had remarkable success in imaging cellular structures with nanometer resolution, but the need for activating only single isolated emitters limits imaging speed and labeling density. Here, we overcome this major limitation using deep learning. We developed DECODE, a computational tool that can localize single emitters at high density in 3D with highest accuracy for a large range of imaging modalities and conditions. In a public software benchmark competition, it outperformed all other fitters on 12 out of 12 data-sets when comparing both detection accuracy and localization error, often by a substantial margin. DECODE allowed us to take live-cell SMLM data with reduced light exposure in just 3 seconds and to image microtubules at ultra-high labeling density. Packaged for simple installation and use, DECODE will enable many labs to reduce imaging times and increase localization density in SMLM.Competing Interest StatementThe authors have declared no competing interest.
The most sophisticated existing methods to generate 3D isotropic super-resolution (SR) from non-isotropic electron microscopy (EM) are based on learned dictionaries. Unfortunately, none of the existing methods generate practically satisfying results. For 2D natural images, recently developed super-resolution methods that use deep learning have been shown to significantly outperform the previous state of the art. We have adapted one of the most successful architectures (FSRCNN) for 3D super-resolution, and compared its performance to a 3D U-Net architecture that has not been used previously to generate super-resolution. We trained both architectures on artificially downscaled isotropic ground truth from focused ion beam milling scanning EM (FIB-SEM) and tested the performance for various hyperparameter settings. Our results indicate that both architectures can successfully generate 3D isotropic super-resolution from non-isotropic EM, with the U-Net performing consistently better. We propose several promising directions for practical application.
Optical aberrations hinder fluorescence microscopy of thick samples, reducing image signal, contrast, and resolution. Here we introduce a deep learning-based strategy for aberration compensation, improving image quality without slowing image acquisition, applying additional dose, or introducing more optics. Our method (i) introduces synthetic aberrations to images acquired on the shallow side of image stacks, making them resemble those acquired deeper into the volume and (ii) trains neural networks to reverse the effect of these aberrations. We use simulations and experiments to show that applying the trained ‘de-aberration’ networks outperforms alternative methods, providing restoration on par with adaptive optics techniques; and subsequently apply the networks to diverse datasets captured with confocal, light-sheet, multi-photon, and super-resolution microscopy. In all cases, the improved quality of the restored data facilitates qualitative image inspection and improves downstream image quantitation, including orientational analysis of blood vessels in mouse tissue and improved membrane and nuclear segmentation in C. elegans embryos.
Limited color channels in fluorescence microscopy have long constrained spatial analysis in biological specimens. Here, we introduce cycle Hybridization Chain Reaction (HCR), a method that integrates multicycle DNA barcoding with HCR to overcome this limitation. cycleHCR enables highly multiplexed imaging of RNA and proteins using a unified barcode system. Whole-embryo transcriptomics imaging achieved precise three-dimensional gene expression and cell fate mapping across a specimen depth of ~310 μm. When combined with expansion microscopy, cycleHCR revealed an intricate network of 10 subcellular structures in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. In mouse hippocampal slices, multiplex RNA and protein imaging uncovered complex gene expression gradients and cell-type-specific nuclear structural variations. cycleHCR provides a quantitative framework for elucidating spatial regulation in deep tissue contexts for research and potentially diagnostic applications. bioRxiv preprint: 10.1101/2024.05.17.594641