Filter
Associated Lab
- Dudman Lab (1) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (1) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (1) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (1) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (2) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (1) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (2) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (1) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (1) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Remove Sternson Lab filter Sternson Lab
- Svoboda Lab (4) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (3) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (1) Apply Turaga Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Publication Date
- 2023 (2) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (3) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (3) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (4) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (2) Apply 2019 filter
- 2017 (2) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (3) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (7) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (5) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (3) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (4) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (6) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (1) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (2) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (1) Apply 2008 filter
- 2005 (1) Apply 2005 filter
- 2004 (1) Apply 2004 filter
- 2002 (1) Apply 2002 filter
- 2001 (2) Apply 2001 filter
- 1998 (1) Apply 1998 filter
Type of Publication
54 Publications
Showing 21-30 of 54 resultsSmall molecules that alter protein function provide a means to modulate biological networks with temporal resolution. Here we demonstrate a potentially general and scalable method of identifying such molecules by application to a particular protein, Ure2p, which represses the transcription factors Gln3p and Nil1p. By probing a high-density microarray of small molecules generated by diversity-oriented synthesis with fluorescently labelled Ure2p, we performed 3,780 protein-binding assays in parallel and identified several compounds that bind Ure2p. One compound, which we call uretupamine, specifically activates a glucose-sensitive transcriptional pathway downstream of Ure2p. Whole-genome transcription profiling and chemical epistasis demonstrate the remarkable Ure2p specificity of uretupamine and its ability to modulate the glucose-sensitive subset of genes downstream of Ure2p. These results demonstrate that diversity-oriented synthesis and small-molecule microarrays can be used to identify small molecules that bind to a protein of interest, and that these small molecules can regulate specific functions of the protein.
Determining the spatial organization and morphological characteristics of molecularly defined cell types is a major bottleneck for characterizing the architecture underpinning brain function. We developed Expansion-Assisted Iterative Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (EASI-FISH) to survey gene expression in brain tissue, as well as a turnkey computational pipeline to rapidly process large EASI-FISH image datasets. EASI-FISH was optimized for thick brain sections (300 μm) to facilitate reconstruction of spatio-molecular domains that generalize across brains. Using the EASI-FISH pipeline, we investigated the spatial distribution of dozens of molecularly defined cell types in the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), a brain region with poorly defined anatomical organization. Mapping cell types in the LHA revealed nine spatially and molecularly defined subregions. EASI-FISH also facilitates iterative reanalysis of scRNA-seq datasets to determine marker-genes that further dissociated spatial and morphological heterogeneity. The EASI-FISH pipeline democratizes mapping molecularly defined cell types, enabling discoveries about brain organization.
Determining the spatial organization and morphological characteristics of molecularly defined cell types is a major bottleneck for characterizing the architecture underpinning brain function. We developed Expansion-Assisted Iterative Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (EASI-FISH) to survey gene expression in brain tissue, as well as a turnkey computational pipeline to rapidly process large EASI-FISH image datasets. EASI-FISH was optimized for thick brain sections (300 µm) to facilitate reconstruction of spatio-molecular domains that generalize across brains. Using the EASI-FISH pipeline, we investigated the spatial distribution of dozens of molecularly defined cell types in the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), a brain region with poorly defined anatomical organization. Mapping cell types in the LHA revealed nine novel spatially and molecularly defined subregions. EASI-FISH also facilitates iterative re-analysis of scRNA-Seq datasets to determine marker-genes that further dissociated spatial and morphological heterogeneity. The EASI-FISH pipeline democratizes mapping molecularly defined cell types, enabling discoveries about brain organization.
The influence of peripheral physiology on goal-directed behavior involves specialized interoceptive sensory neurons that signal internal state to the brain. Here, we review recent progress to examine the impact of these specialized cell types on neurons and circuits throughout the central nervous system. These new approaches are important for understanding how the needs of the body interact and guide goal-directed behaviors.
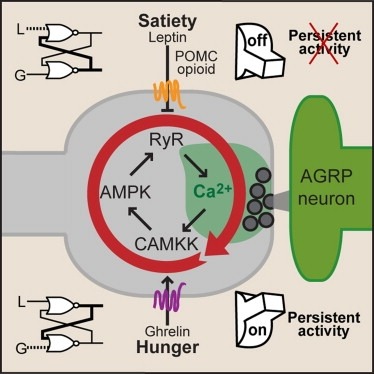
Synaptic plasticity in response to changes in physiologic state is coordinated by hormonal signals across multiple neuronal cell types, but the significance and underlying mechanisms are unclear. Here, we combine cell type-specific electrophysiological, pharmacological, and optogenetic techniques to dissect neural circuits and molecular pathways controlling synaptic plasticity onto AGRP neurons, a population that regulates feeding. We find that food deprivation elevates excitatory synaptic input, which is mediated by a presynaptic positive feedback loop involving AMP-activated protein kinase. Potentiation of glutamate release was triggered by the orexigenic hormone ghrelin and exhibited hysteresis, persisting for hours after ghrelin removal. Persistent activity was reversed by the anorexigenic hormone leptin, and optogenetic photostimulation demonstrated involvement of opioid release from POMC neurons. Based on these experiments, we propose a memory storage device for physiological state constructed from bistable synapses that are flipped between two sustained activity states by transient exposure to hormones signaling energy levels. Supported by: Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
This chapter reviews the application of new genetically encoded tools in feeding circuits that regulate appetite. Rapid activation and inhibition of agouti related peptide (AgRP) neurons conclusively established a causal role for rapid control of food intake. Chemogenetic activation of AgRP neurons using hM3Dq avoids the invasive protocols required for ChR2 activation. ChR2 distributes into axons, and selective optogenetic activation of AgRP neuron axon projection fields in distinct brain areas was used to examine their individual contribution to feeding behavior. Some of the brain areas targeted by AgRP neuron axon projections have been examined further for cell type specific control of appetite. Rodents with bed nucleus of stria terminalis (BNST) lesions show hyperphagia and obesity, indicating that reduced BNST output promotes feeding. pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons regulate feeding over longer timescales. parabrachial nucleus (PBN) neurons have a powerful inhibitory role on food intake, but their inhibition does not strongly elevate food intake.
Hunger and thirst have distinct goals but control similar ingestive behaviors, and little is known about neural processes that are shared between these behavioral states. We identify glutamatergic neurons in the peri-locus coeruleus (periLC neurons) as a polysynaptic convergence node from separate energy-sensitive and hydration-sensitive cell populations. We develop methods for stable hindbrain calcium imaging in free-moving mice, which show that periLC neurons are tuned to ingestive behaviors and respond similarly to food or water consumption. PeriLC neurons are scalably inhibited by palatability and homeostatic need during consumption. Inhibition of periLC neurons is rewarding and increases consumption by enhancing palatability and prolonging ingestion duration. These properties comprise a double-negative feedback relationship that sustains food or water consumption without affecting food- or water-seeking. PeriLC neurons are a hub between hunger and thirst that specifically controls motivation for food and water ingestion, which is a factor that contributes to hedonic overeating and obesity.
Physiological need states direct decision-making toward re-establishing homeostasis. Using a two-alternative forced choice task for mice that models elements of human decisions, we found that varying hunger and thirst states caused need-inappropriate choices, such as food seeking when thirsty. These results show limits on interoceptive knowledge of hunger and thirst states to guide decision-making. Instead, need states were identified after food and water consumption by outcome evaluation, which depended on the medial prefrontal cortex.
Synaptic plasticity in response to changes in physiologic state is coordinated by hormonal signals across multiple neuronal cell types. Here, we combine cell-type-specific electrophysiological, pharmacological, and optogenetic techniques to dissect neural circuits and molecular pathways controlling synaptic plasticity onto AGRP neurons, a population that regulates feeding. We find that food deprivation elevates excitatory synaptic input, which is mediated by a presynaptic positive feedback loop involving AMP-activated protein kinase. Potentiation of glutamate release was triggered by the orexigenic hormone ghrelin and exhibited hysteresis, persisting for hours after ghrelin removal. Persistent activity was reversed by the anorexigenic hormone leptin, and optogenetic photostimulation demonstrated involvement of opioid release from POMC neurons. Based on these experiments, we propose a memory storage device for physiological state constructed from bistable synapses that are flipped between two sustained activity states by transient exposure to hormones signaling energy levels.