Filter
Associated Lab
- Ahrens Lab (1) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (2) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (2) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (5) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Bock Lab (1) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (3) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (1) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (6) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (1) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Cui Lab (6) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (3) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (3) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (1) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (1) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (1) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (7) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (7) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (3) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (9) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hess Lab (3) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (2) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (2) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Kainmueller Lab (2) Apply Kainmueller Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (1) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (2) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (3) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (1) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (4) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (2) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (2) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (12) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Looger Lab (13) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (6) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (1) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (1) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (1) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (1) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (1) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (1) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (1) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (8) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (7) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (2) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (3) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (2) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (1) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (1) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (11) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (4) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (5) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (4) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (9) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (1) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (1) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (3) Apply Truman Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Publication Date
- December 2012 (16) Apply December 2012 filter
- November 2012 (16) Apply November 2012 filter
- October 2012 (23) Apply October 2012 filter
- September 2012 (6) Apply September 2012 filter
- August 2012 (13) Apply August 2012 filter
- July 2012 (9) Apply July 2012 filter
- June 2012 (15) Apply June 2012 filter
- May 2012 (13) Apply May 2012 filter
- April 2012 (14) Apply April 2012 filter
- March 2012 (10) Apply March 2012 filter
- February 2012 (19) Apply February 2012 filter
- January 2012 (36) Apply January 2012 filter
- Remove 2012 filter 2012
Type of Publication
190 Publications
Showing 61-70 of 190 resultsDirected cell motility is at the basis of biological phenomena such as development, wound healing, and metastasis. It has been shown that substrate attachments mediate motility by coupling the cell's cytoskeleton with force generation. However, it has been unclear how the persistence of cell directionality is facilitated. We show that mRNA localization plays an important role in this process, but the mechanism of action is still unknown. In this study, we show that the zipcode-binding protein 1 transports β-actin mRNA to the focal adhesion compartment, where it dwells for minutes, suggesting a means for associating its localization with motility through the formation of stable connections between adhesions and newly synthesized actin filaments. In order to demonstrate this, we developed an approach for assessing the functional consequences of β-actin mRNA and protein localization by tethering the mRNA to a specific location-in this case, the focal adhesion complex. This approach will have a significant impact on cell biology because it is now possible to forcibly direct any mRNA and its cognate protein to specific locations in the cell. This will reveal the importance of localized protein translation on various cellular processes.
Animals approach stimuli that predict a pleasant outcome. After the paired presentation of an odour and a reward, Drosophila melanogaster can develop a conditioned approach towards that odour. Despite recent advances in understanding the neural circuits for associative memory and appetitive motivation, the cellular mechanisms for reward processing in the fly brain are unknown. Here we show that a group of dopamine neurons in the protocerebral anterior medial (PAM) cluster signals sugar reward by transient activation and inactivation of target neurons in intact behaving flies. These dopamine neurons are selectively required for the reinforcing property of, but not a reflexive response to, the sugar stimulus. In vivo calcium imaging revealed that these neurons are activated by sugar ingestion and the activation is increased on starvation. The output sites of the PAM neurons are mainly localized to the medial lobes of the mushroom bodies (MBs), where appetitive olfactory associative memory is formed. We therefore propose that the PAM cluster neurons endow a positive predictive value to the odour in the MBs. Dopamine in insects is known to mediate aversive reinforcement signals. Our results highlight the cellular specificity underlying the various roles of dopamine and the importance of spatially segregated local circuits within the MBs.
Rab proteins are important regulators of insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane (PM), but the precise steps in GLUT4 trafficking modulated by particular Rab proteins remain unclear. Here, we systematically investigate the involvement of Rab proteins in GLUT4 trafficking, focusing on Rab proteins directly mediating GLUT4 storage vesicle (GSV) delivery to the PM. Using dual-color total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy and an insulin-responsive aminopeptidase (IRAP)-pHluorin fusion assay, we demonstrated that Rab10 directly facilitated GSV translocation to and docking at the PM. Rab14 mediated GLUT4 delivery to the PM via endosomal compartments containing transferrin receptor (TfR), whereas Rab4A, Rab4B, and Rab8A recycled GLUT4 through the endosomal system. Myosin-Va associated with GSVs by interacting with Rab10, positioning peripherally recruited GSVs for ultimate fusion. Thus, multiple Rab proteins regulate the trafficking of GLUT4, with Rab10 coordinating with myosin-Va to mediate the final steps of insulin-stimulated GSV translocation to the PM.
The conserved Ndc80 complex is an essential microtubule-binding component of the kinetochore. Recent findings suggest that the Ndc80 complex influences microtubule dynamics at kinetochores in vivo. However, it was unclear if the Ndc80 complex mediates these effects directly, or by affecting other factors localized at the kinetochore. Using a reconstituted system in vitro, we show that the human Ndc80 complex directly stabilizes the tips of disassembling microtubules and promotes rescue (the transition from microtubule shortening to growth). In vivo, an N-terminal domain in the Ndc80 complex is phosphorylated by the Aurora B kinase. Mutations that mimic phosphorylation of the Ndc80 complex prevent stable kinetochore-microtubule attachment, and mutations that block phosphorylation damp kinetochore oscillations. We find that the Ndc80 complex with Aurora B phosphomimetic mutations is defective at promoting microtubule rescue, even when robustly coupled to disassembling microtubule tips. This impaired ability to affect dynamics is not simply because of weakened microtubule binding, as an N-terminally truncated complex with similar binding affinity is able to promote rescue. Taken together, these results suggest that in addition to regulating attachment stability, Aurora B controls microtubule dynamics through phosphorylation of the Ndc80 complex.
The origin of the spatial receptive fields of hippocampal place cells has not been established. A hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell receives thousands of synaptic inputs, mostly from other spatially tuned neurons; however, how the postsynaptic neuron’s cellular properties determine the response to these inputs during behavior is unknown. We discovered that, contrary to expectations from basic models of place cells and neuronal integration, a small, spatially uniform depolarization of the spatially untuned somatic membrane potential of a silent cell leads to the sudden and reversible emergence of a spatially tuned subthreshold response and place-field spiking. Such gating of inputs by postsynaptic neuronal excitability reveals a cellular mechanism for receptive field origin and may be critical for the formation of hippocampal memory representations.
Recent behavioral studies have given rise to two contrasting models for limited working memory capacity: a "discrete-slot" model in which memory items are stored in a limited number of slots, and a "shared-resource" model in which the neural representation of items is distributed across a limited pool of resources. To elucidate the underlying neural processes, we investigated a continuous network model for working memory of an analog feature. Our model network fundamentally operates with a shared resource mechanism, and stimuli in cue arrays are encoded by a distributed neural population. On the other hand, the network dynamics and performance are also consistent with the discrete-slot model, because multiple objects are maintained by distinct localized population persistent activity patterns (bump attractors). We identified two phenomena of recurrent circuit dynamics that give rise to limited working memory capacity. As the working memory load increases, a localized persistent activity bump may either fade out (so the memory of the corresponding item is lost) or merge with another nearby bump (hence the resolution of mnemonic representation for the merged items becomes blurred). We identified specific dependences of these two phenomena on the strength and tuning of recurrent synaptic excitation, as well as network normalization: the overall population activity is invariant to set size and delay duration; therefore, a constant neural resource is shared by and dynamically allocated to the memorized items. We demonstrate that the model reproduces salient observations predicted by both discrete-slot and shared-resource models, and propose testable predictions of the merging phenomenon.
Background: It is unclear whether long-term seizure outcomes in children are similar to those in adult epilepsy surgery patients. Objective: To determine 5-year outcomes and antiepilepsy drug (AED) use in pediatric epilepsy surgery patients from a single institution. Methods: The cohort consisted of children younger than 18 years of age whose 5-year outcome data would have been available by 2010. Comparisons were made between patients with and without 5-year data (n = 338), patients with 5-year data for seizure outcome (n = 257), and seizure-free patients on and off AEDs (n = 137). Results: Five-year data were available from 76% of patients. More seizure-free patients with focal resections for hippocampal sclerosis and tumors lacked 5-year data compared with other cases. Of those with 5-year data, 53% were continuously seizure free, 18% had late seizure recurrence, 3% became seizure free after initial failure, and 25% were never seizure free. Patients were more likely to be continuously seizure free if their surgery was performed during the period 2001 to 2005 (68%) compared with surgery performed from 1996 to 2000 (61%), 1991 to 1995 (36%), and 1986 to 1990 (46%). More patients had 1 or fewer seizures per month in the late seizure recurrence (47%) compared with the not seizure-free group (20%). Four late deaths occurred in the not seizure-free group compared with 1 in the seizure-free group. Of patients who were continuously seizure free, 55% were not taking AEDs, and more cortical dysplasia patients (74%) had stopped taking AEDs compared with hemimegalencephaly patients (18%). Conclusion: In children, 5-year outcomes improved over 20 years of clinical experience. Our results are similar to those of adult epilepsy surgery patients despite mostly extratemporal and hemispheric operations for diverse developmental etiologies.
Chromosomes must be accurately partitioned to daughter cells to prevent aneuploidy, a hallmark of many tumors and birth defects. Kinetochores are the macromolecular machines that segregate chromosomes by maintaining load-bearing attachments to the dynamic tips of microtubules. Here, we present the structure of isolated budding-yeast kinetochore particles, as visualized by EM and electron tomography of negatively stained preparations. The kinetochore appears as an 126-nm particle containing a large central hub surrounded by multiple outer globular domains. In the presence of microtubules, some particles also have a ring that encircles the microtubule. Our data, showing that kinetochores bind to microtubules via multivalent attachments, lay the foundation to uncover the key mechanical and regulatory mechanisms by which kinetochores control chromosome segregation and cell division.
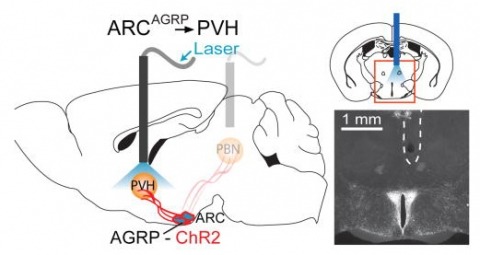
Hunger is a complex behavioural state that elicits intense food seeking and consumption. These behaviours are rapidly recapitulated by activation of starvation-sensitive AGRP neurons, which present an entry point for reverse-engineering neural circuits for hunger. Here we mapped synaptic interactions of AGRP neurons with multiple cell populations in mice and probed the contribution of these distinct circuits to feeding behaviour using optogenetic and pharmacogenetic techniques. An inhibitory circuit with paraventricular hypothalamus (PVH) neurons substantially accounted for acute AGRP neuron-evoked eating, whereas two other prominent circuits were insufficient. Within the PVH, we found that AGRP neurons target and inhibit oxytocin neurons, a small population that is selectively lost in Prader-Willi syndrome, a condition involving insatiable hunger. By developing strategies for evaluating molecularly defined circuits, we show that AGRP neuron suppression of oxytocin neurons is critical for evoked feeding. These experiments reveal a new neural circuit that regulates hunger state and pathways associated with overeating disorders.
Bacteriophage HK97 maturation involves discrete intermediate particle forms, comparable to transitional states in protein folding, before reaching its mature form. The process starts by formation of a metastable prohead, poised for exothermic expansion triggered by DNA packaging. During maturation, the capsid subunit transitions from a strained to a canonical tertiary conformation and this has been postulated to be the driving mechanism for initiating expansion via switching hexameric capsomer architecture from skewed to 6-fold symmetric. We report the subnanometer electron-cryomicroscopy reconstruction of the HK97 first expansion intermediate before any crosslink formation. This form displays 6-fold symmetric hexamers, but capsid subunit tertiary structures exhibit distortions comparable to the prohead forms. We propose that coat subunit strain release acts in synergy with the first crosslinks to drive forward maturation. Finally, we speculate that the energetic features of this transition may result from increased stability of intermediates during maturation via enhanced inter-subunit interactions.