Filter
Associated Lab
- Aso Lab (1) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Remove Betzig Lab filter Betzig Lab
- Bock Lab (1) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (1) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (2) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Harris Lab (2) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Hess Lab (6) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ji Lab (11) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (8) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (6) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (6) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Magee Lab (2) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (1) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (2) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (1) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (9) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Singer Lab (1) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (2) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (4) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Turner Lab (1) Apply Turner Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Associated Support Team
- Electron Microscopy (2) Apply Electron Microscopy filter
- Integrative Imaging (1) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Janelia Experimental Technology (1) Apply Janelia Experimental Technology filter
- Molecular Genomics (1) Apply Molecular Genomics filter
- Primary & iPS Cell Culture (1) Apply Primary & iPS Cell Culture filter
- Project Technical Resources (1) Apply Project Technical Resources filter
- Scientific Computing Software (1) Apply Scientific Computing Software filter
- Viral Tools (1) Apply Viral Tools filter
Publication Date
- 2024 (1) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (4) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (3) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (2) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (4) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (7) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (6) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (8) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (12) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (11) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (8) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (4) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (5) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (7) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (3) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (2) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (8) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (2) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (1) Apply 2006 filter
98 Janelia Publications
Showing 51-60 of 98 resultsLight sheet microscopy is a powerful technique for visualizing dynamic biological processes in 3D. Studying large specimens or recording time series with high spatial and temporal resolution generates large datasets, often exceeding terabytes and potentially reaching petabytes in size. Handling these massive datasets is challenging for conventional data processing tools with their memory and performance limitations. To overcome these issues, we developed LLSM5DTools, a software solution specifically designed for the efficient management of petabyte-scale light sheet microscopy data. This toolkit, optimized for memory and per-formance, features fast image readers and writers, efficient geometric transformations, high-performance Richardson-Lucy deconvolution, and scalable Zarr-based stitching. These advancements enable LLSM5DTools to perform over ten times faster than current state-of-the-art methods, facilitating real-time processing of large datasets and opening new avenues for biological discoveries in large-scale imaging experiments.
We introduce a method for optically imaging intracellular proteins at nanometer spatial resolution. Numerous sparse subsets of photoactivatable fluorescent protein molecules were activated, localized (to approximately 2 to 25 nanometers), and then bleached. The aggregate position information from all subsets was then assembled into a superresolution image. We used this method–termed photoactivated localization microscopy–to image specific target proteins in thin sections of lysosomes and mitochondria; in fixed whole cells, we imaged vinculin at focal adhesions, actin within a lamellipodium, and the distribution of the retroviral protein Gag at the plasma membrane.
Commentary: The original PALM paper by myself and my friend and co-inventor Harald Hess, spanning the before- and after-HHMI eras. Submitted and publicly presented months before other publications in the same year, the lessons of the paper remain widely misunderstood: 1) localization precision is not resolution; 2) the ability to resolve a few molecules by the Rayleigh criterion in a diffraction limited region (DLR) does not imply the ability to resolve structures of arbitrary complexity at the same scale; 3) true resolution well beyond the Abbe limit requires the ability to isolate and localize hundreds or thousands of molecules in one DLR; and 4) certain photoactivatable fluorescent proteins (PA-FPs) and caged dyes can be isolated and precisely localized at such densities; yielding true resolution down to 20 nm. The molecular densities we demonstrate (105 molecules/m2) are more than two orders of magnitude greater than in later papers that year (implying ten-fold better true resolution) – indeed, these papers demonstrate densities only comparable to earlier spectral or photobleaching based isolation methods. We validate our claims by correlative electron microscopy, and demonstrate the outstanding advantages of PA-FPs for superresolution microscopy: minimally perturbative sample preparation; high labeling densities; close binding to molecular targets; and zero non-specific background.
Observation of molecular processes inside living cells is fundamental to a quantitative understanding of how biological systems function. Specifically, decoding the complex behavior of single molecules enables us to measure kinetics, transport, and self-assembly at this fundamental level that is often veiled in ensemble experiments. In the past decade, rapid developments in fluorescence microscopy, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, and fluorescent labeling techniques have enabled new experiments to investigate the robustness and stochasticity of diverse molecular mechanisms with high spatiotemporal resolution. This review discusses the concepts and strategies of structural and functional imaging in living cells at the single-molecule level with minimal perturbations to the specimen.
The diffraction limited resolution of two photon and confocal microscope can be recovered using adaptive optics to explore the detailed neuronal network in the brains of zebrafish and mouse in vivo.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an expansive, membrane-enclosed organelle that plays crucial roles in numerous cellular functions. We used emerging superresolution imaging technologies to clarify the morphology and dynamics of the peripheral ER, which contacts and modulates most other intracellular organelles. Peripheral components of the ER have classically been described as comprising both tubules and flat sheets. We show that this system consists almost exclusively of tubules at varying densities, including structures that we term ER matrices. Conventional optical imaging technologies had led to misidentification of these structures as sheets because of the dense clustering of tubular junctions and a previously uncharacterized rapid form of ER motion. The existence of ER matrices explains previous confounding evidence that had indicated the occurrence of ER “sheet” proliferation after overexpression of tubular junction–forming proteins.
In an interferometer-based fluorescence microscope, a beam splitter is often used to combine two emission wavefronts interferometrically. There are two perpendicular paths along which the interference fringes can propagate and normally only one is used for imaging. However, the other path also contains useful information. Here we introduced a second camera to our interferometer-based three-dimensional structured-illumination microscope (I(5)S) to capture the fringes along the normally unused path, which are out of phase by π relative to the fringes along the other path. Based on this complementary phase relationship and the well-defined phase interrelationships among the I(5)S data components, we can deduce and then computationally eliminate the path length errors within the interferometer loop using the simultaneously recorded fringes along the two imaging paths. This self-correction capability can greatly relax the requirement for eliminating the path length differences before and maintaining that status during each imaging session, which are practically challenging tasks. Experimental data is shown to support the theory.
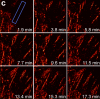
The inner ear is a fluid-filled closed-epithelial structure whose function requires maintenance of an internal hydrostatic pressure and fluid composition. The endolymphatic sac (ES) is a dead-end epithelial tube connected to the inner ear whose function is unclear. ES defects can cause distended ear tissue, a pathology often seen in hearing and balance disorders. Using live imaging of zebrafish larvae, we reveal that the ES undergoes cycles of slow pressure-driven inflation followed by rapid deflation. Absence of these cycles in mutants leads to distended ear tissue. Using serial-section electron microscopy and adaptive optics lattice light-sheet microscopy, we find a pressure relief valve in the ES comprised of partially separated apical junctions and dynamic overlapping basal lamellae that separate under pressure to release fluid. We propose that this lmx1-dependent pressure relief valve is required to maintain fluid homeostasis in the inner ear and other fluid-filled cavities.
Although fluorescence microscopy provides a crucial window into the physiology of living specimens, many biological processes are too fragile, are too small, or occur too rapidly to see clearly with existing tools. We crafted ultrathin light sheets from two-dimensional optical lattices that allowed us to image three-dimensional (3D) dynamics for hundreds of volumes, often at subsecond intervals, at the diffraction limit and beyond. We applied this to systems spanning four orders of magnitude in space and time, including the diffusion of single transcription factor molecules in stem cell spheroids, the dynamic instability of mitotic microtubules, the immunological synapse, neutrophil motility in a 3D matrix, and embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster. The results provide a visceral reminder of the beauty and the complexity of living systems.
We demonstrate live-cell super-resolution imaging using photoactivated localization microscopy (PALM). The use of photon-tolerant cell lines in combination with the high resolution and molecular sensitivity of PALM permitted us to investigate the nanoscale dynamics within individual adhesion complexes (ACs) in living cells under physiological conditions for as long as 25 min, with half of the time spent collecting the PALM images at spatial resolutions down to approximately 60 nm and frame rates as short as 25 s. We visualized the formation of ACs and measured the fractional gain and loss of individual paxillin molecules as each AC evolved. By allowing observation of a wide variety of nanoscale dynamics, live-cell PALM provides insights into molecular assembly during the initiation, maturation and dissolution of cellular processes.
Commentary: The first example of true live cell and time lapse imaging by localization microscopy (as opposed to particle tracking), this paper uses the Nyquist criterion to establish a necessary condition for true spatial resolution based on the density of localized molecules – a condition often unmet in claims elsewhere in the superresolution literature.
By any method, higher spatiotemporal resolution requires increasing light exposure at the specimen, making noninvasive imaging increasingly difficult. Here, simultaneous differential interference contrast imaging is used to establish that cells behave physiologically before, during, and after PALM imaging. Similar controls are lacking from many supposed “live cell” superresolution demonstrations.