Filter
Associated Lab
- Ahrens Lab (2) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Baker Lab (1) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (3) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Harris Lab (3) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (7) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (1) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Remove Jayaraman Lab filter Jayaraman Lab
- Ji Lab (1) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (1) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Looger Lab (10) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (1) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (2) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Romani Lab (4) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (5) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (1) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (1) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (9) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (9) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (1) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Associated Support Team
- Anatomy and Histology (1) Apply Anatomy and Histology filter
- Fly Facility (2) Apply Fly Facility filter
- Janelia Experimental Technology (6) Apply Janelia Experimental Technology filter
- Molecular Genomics (1) Apply Molecular Genomics filter
- Primary & iPS Cell Culture (1) Apply Primary & iPS Cell Culture filter
- Project Technical Resources (1) Apply Project Technical Resources filter
- Scientific Computing Software (3) Apply Scientific Computing Software filter
- Scientific Computing Systems (1) Apply Scientific Computing Systems filter
Publication Date
- 2024 (1) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (1) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (3) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (1) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (4) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (4) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (3) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (4) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (3) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (4) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (1) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (3) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (2) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (2) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (2) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (1) Apply 2009 filter
39 Janelia Publications
Showing 31-39 of 39 resultsCognition encompasses a range of higher-order mental processes, such as attention, working memory, and model-based decision-making. These processes are thought to involve the dynamic interaction of multiple central brain regions. A mechanistic understanding of such computations requires not only monitoring and manipulating specific neural populations during behavior, but also knowing the connectivity of the underlying circuitry. These goals are experimentally challenging in mammals, but are feasible in numerically simpler insect brains. In Drosophila melanogaster in particular, genetic tools enable precisely targeted physiology and optogenetics in actively behaving animals. In this article we discuss how these advantages are increasingly being leveraged to study abstract neural representations and sensorimotor computations that may be relevant for cognition in both insects and mammals.
Hordes of tourists flock to Washington, D.C. every spring to see the cherry trees blossom. Once in the city, they must find their way to the Tidal Basin where the Japanese trees grow. Fortunately, a number of visual landmarks can help them to navigate. In 1910, the United States Congress passed The Height of Buildings Act, limiting the elevation of commercial and residential structures in D.C. to 130 feet. Thus, the 555-foot-tall Washington Monument often looms large against the horizon, serving as an anchor point to help set the tourists' sense of direction. Once their heading is set, they can lose sight of the monument behind buildings or groups of tall Scandinavian visitors and still use their internal compass to navigate to the Basin. This compass keeps track of their paces and turns and updates their sense of where they are and where they need to go. Yet while their heading informs their actions, it does not dictate them. Tourists who have been to D.C. in the past can, for example, use remembered views to alter their routes to avoid crowds. On an even finer scale, their leg movements also depend on their current state - they might increase the frequency and length of their strides if hunger pangs compete with their desire to see cherry blossoms, for example. The way in which these disparate cues and motivations influence exploration is a neuroscience mystery across creatures large and small.
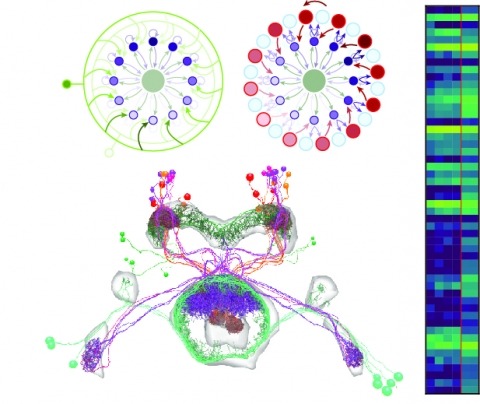
Neural representations of head direction (HD) have been discovered in many species. Theoretical work has proposed that the dynamics associated with these representations are generated, maintained, and updated by recurrent network structures called ring attractors. We evaluated this theorized structure-function relationship by performing electron-microscopy-based circuit reconstruction and RNA profiling of identified cell types in the HD system of Drosophila melanogaster. We identified motifs that have been hypothesized to maintain the HD representation in darkness, update it when the animal turns, and tether it to visual cues. Functional studies provided support for the proposed roles of individual excitatory or inhibitory circuit elements in shaping activity. We also discovered recurrent connections between neuronal arbors with mixed pre- and postsynaptic specializations. Our results confirm that the Drosophila HD network contains the core components of a ring attractor while also revealing unpredicted structural features that might enhance the network's computational power.
Drosophila melanogaster is a model organism rich in genetic tools to manipulate and identify neural circuits involved in specific behaviors. Here we present a technique for two-photon calcium imaging in the central brain of head-fixed Drosophila walking on an air-supported ball. The ball’s motion is tracked at high resolution and can be treated as a proxy for the fly’s own movements. We used the genetically encoded calcium sensor, GCaMP3.0, to record from important elements of the motion-processing pathway, the horizontal-system lobula plate tangential cells (LPTCs) in the fly optic lobe. We presented motion stimuli to the tethered fly and found that calcium transients in horizontal-system neurons correlated with robust optomotor behavior during walking. Our technique allows both behavior and physiology in identified neurons to be monitored in a genetic model organism with an extensive repertoire of walking behaviors.
Fluorescent calcium sensors are widely used to image neural activity. Using structure-based mutagenesis and neuron-based screening, we developed a family of ultrasensitive protein calcium sensors (GCaMP6) that outperformed other sensors in cultured neurons and in zebrafish, flies and mice in vivo. In layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons of the mouse visual cortex, GCaMP6 reliably detected single action potentials in neuronal somata and orientation-tuned synaptic calcium transients in individual dendritic spines. The orientation tuning of structurally persistent spines was largely stable over timescales of weeks. Orientation tuning averaged across spine populations predicted the tuning of their parent cell. Although the somata of GABAergic neurons showed little orientation tuning, their dendrites included highly tuned dendritic segments (5–40-µm long). GCaMP6 sensors thus provide new windows into the organization and dynamics of neural circuits over multiple spatial and temporal scales.
Neurons and neural networks often extend hundreds of micrometers in three dimensions. Capturing the calcium transients associated with their activity requires volume imaging methods with subsecond temporal resolution. Such speed is a challenge for conventional two-photon laser-scanning microscopy, because it depends on serial focal scanning in 3D and indicators with limited brightness. Here we present an optical module that is easily integrated into standard two-photon laser-scanning microscopes to generate an axially elongated Bessel focus, which when scanned in 2D turns frame rate into volume rate. We demonstrated the power of this approach in enabling discoveries for neurobiology by imaging the calcium dynamics of volumes of neurons and synapses in fruit flies, zebrafish larvae, mice and ferrets in vivo. Calcium signals in objects as small as dendritic spines could be resolved at video rates, provided that the samples were sparsely labeled to limit overlap in their axially projected images.
The visual neurons of many animals process sensory input differently depending on the animal’s state of locomotion. Now, new work in Drosophila melanogaster shows that neuromodulatory neurons active during flight boost responses of neurons in the visual system.
Studying the intertwined roles of sensation, experience, and directed action in navigation has been facilitated by the development of virtual reality (VR) environments for head-fixed animals, allowing for quantitative measurements of behavior in well-controlled conditions. VR has long featured in studies of Drosophila melanogaster, but these experiments have typically allowed the fly to change only its heading in a visual scene and not its position. Here we explore how flies move in two dimensions (2D) using a visual VR environment that more closely captures an animal's experience during free behavior. We show that flies' 2D interaction with landmarks cannot be automatically derived from their orienting behavior under simpler one-dimensional (1D) conditions. Using novel paradigms, we then demonstrate that flies in 2D VR adapt their behavior in response to optogenetically delivered appetitive and aversive stimuli. Much like free-walking flies after encounters with food, head-fixed flies exploring a 2D VR respond to optogenetic activation of sugar-sensing neurons by initiating a local search, which appears not to rely on visual landmarks. Visual landmarks can, however, help flies to avoid areas in VR where they experience an aversive, optogenetically generated heat stimulus. By coupling aversive virtual heat to the flies' presence near visual landmarks of specific shapes, we elicit selective learned avoidance of those landmarks. Thus, we demonstrate that head-fixed flies adaptively navigate in 2D virtual environments, but their reliance on visual landmarks is context dependent. These behavioral paradigms set the stage for interrogation of the fly brain circuitry underlying flexible navigation in complex multisensory environments.
Changes in behavioral state modify neural activity in many systems. In some vertebrates such modulation has been observed and interpreted in the context of attention and sensorimotor coordinate transformations. Here we report state-dependent activity modulations during walking in a visual-motor pathway of Drosophila. We used two-photon imaging to monitor intracellular calcium activity in motion-sensitive lobula plate tangential cells (LPTCs) in head-fixed Drosophila walking on an air-supported ball. Cells of the horizontal system (HS)–a subgroup of LPTCs–showed stronger calcium transients in response to visual motion when flies were walking rather than resting. The amplified responses were also correlated with walking speed. Moreover, HS neurons showed a relatively higher gain in response strength at higher temporal frequencies, and their optimum temporal frequency was shifted toward higher motion speeds. Walking-dependent modulation of HS neurons in the Drosophila visual system may constitute a mechanism to facilitate processing of higher image speeds in behavioral contexts where these speeds of visual motion are relevant for course stabilization.