Filter
Associated Lab
- Remove Hermundstad Lab filter Hermundstad Lab
- Jayaraman Lab (7) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Looger Lab (1) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Romani Lab (2) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (2) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (1) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (1) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (1) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Associated Support Team
17 Janelia Publications
Showing 11-17 of 17 resultsInternal representations are thought to support the generation of flexible, long-timescale behavioral patterns in both animals and artificial agents. Here, we present a novel conceptual framework for how Drosophila use their internal representation of head direction to maintain preferred headings in their surroundings, and how they learn to modify these preferences in the presence of selective thermal reinforcement. To develop the framework, we analyzed flies’ behavior in a classical operant visual learning paradigm and found that they use stochastically generated fixations and directed turns to express their heading preferences. Symmetries in the visual scene used in the paradigm allowed us to expose how flies’ probabilistic behavior in this setting is tethered to their head direction representation. We describe how flies’ ability to quickly adapt their behavior to the rules of their environment may rest on a behavioral policy whose parameters are flexible but whose form is genetically encoded in the structure of their circuits. Many of the mechanisms we outline may also be relevant for rapidly adaptive behavior driven by internal representations in other animals, including mammals.
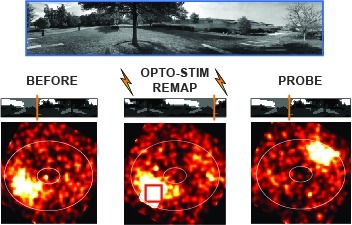
Many animals rely on an internal heading representation when navigating in varied environments. How this representation is linked to the sensory cues that define different surroundings is unclear. In the fly brain, heading is represented by 'compass' neurons that innervate a ring-shaped structure known as the ellipsoid body. Each compass neuron receives inputs from 'ring' neurons that are selective for particular visual features; this combination provides an ideal substrate for the extraction of directional information from a visual scene. Here we combine two-photon calcium imaging and optogenetics in tethered flying flies with circuit modelling, and show how the correlated activity of compass and visual neurons drives plasticity, which flexibly transforms two-dimensional visual cues into a stable heading representation. We also describe how this plasticity enables the fly to convert a partial heading representation, established from orienting within part of a novel setting, into a complete heading representation. Our results provide mechanistic insight into the memory-related computations that are essential for flexible navigation in varied surroundings.
Hunger and thirst have distinct goals but control similar ingestive behaviors, and little is known about neural processes that are shared between these behavioral states. We identify glutamatergic neurons in the peri-locus coeruleus (periLC neurons) as a polysynaptic convergence node from separate energy-sensitive and hydration-sensitive cell populations. We develop methods for stable hindbrain calcium imaging in free-moving mice, which show that periLC neurons are tuned to ingestive behaviors and respond similarly to food or water consumption. PeriLC neurons are scalably inhibited by palatability and homeostatic need during consumption. Inhibition of periLC neurons is rewarding and increases consumption by enhancing palatability and prolonging ingestion duration. These properties comprise a double-negative feedback relationship that sustains food or water consumption without affecting food- or water-seeking. PeriLC neurons are a hub between hunger and thirst that specifically controls motivation for food and water ingestion, which is a factor that contributes to hedonic overeating and obesity.
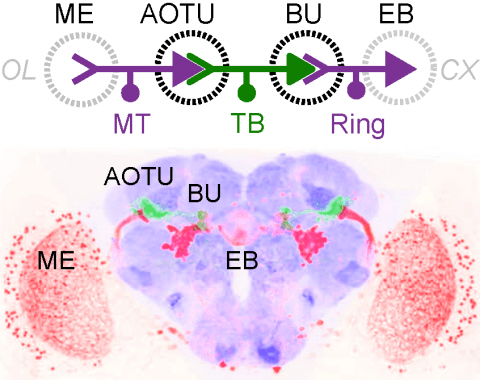
Many animals rely on a representation of head direction for flexible, goal-directed navigation. In insects, a compass-like head direction representation is maintained in a conserved brain region called the central complex. This head direction representation is updated by self-motion information and by tethering to sensory cues in the surroundings through a plasticity mechanism. However, under natural settings, some of these sensory cues may temporarily disappear—for example, when clouds hide the sun—and prominent landmarks at different distances from the insect may move across the animal's field of view during translation, creating potential conflicts for a neural compass. We used two-photon calcium imaging in head-fixed Drosophila behaving in virtual reality to monitor the fly's compass during navigation in immersive naturalistic environments with approachable local landmarks. We found that the fly's compass remains stable even in these settings by tethering to available global cues, likely preserving the animal's ability to perform compass-driven behaviors such as maintaining a constant heading.
Many animals orient using visual cues, but how a single cue is selected from among many is poorly understood. Here we show that Drosophila ring neurons—central brain neurons implicated in navigation—display visual stimulus selection. Using in vivo two-color two-photon imaging with genetically encoded calcium indicators, we demonstrate that individual ring neurons inherit simple-cell-like receptive fields from their upstream partners. Stimuli in the contralateral visual field suppressed responses to ipsilateral stimuli in both populations. Suppression strength depended on when and where the contralateral stimulus was presented, an effect stronger in ring neurons than in their upstream inputs. This history-dependent effect on the temporal structure of visual responses, which was well modeled by a simple biphasic filter, may determine how visual references are selected for the fly's internal compass. Our approach highlights how two-color calcium imaging can help identify and localize the origins of sensory transformations across synaptically connected neural populations.
To interpret the sensory environment, the brain combines ambiguous sensory measurements with context-specific prior experience. But environmental contexts can change abruptly and unpredictably, resulting in uncertainty about the current context. Here we address two questions: how should context-specific prior knowledge optimally guide the interpretation of sensory stimuli in changing environments, and do human decision-making strategies resemble this optimum? We probe these questions with a task in which subjects report the orientation of ambiguous visual stimuli that were drawn from three dynamically switching distributions, representing different environmental contexts. We derive predictions for an ideal Bayesian observer that leverages the statistical structure of the task to maximize decision accuracy and show that its decisions are biased by task context. The magnitude of this decision bias is not a fixed property of the sensory measurement but depends on the observer's belief about the current context. The model therefore predicts that decision bias will grow with the reliability of the context cue, the stability of the environment, and with the number of trials since the last context switch. Analysis of human choice data validates all three predictions, providing evidence that the brain continuously updates probabilistic representations of the environment to best interpret an uncertain, ever-changing world.
Identifying coordinated activity within complex systems is essential to linking their structure and function. We study collective activity in networks of pulse-coupled oscillators that have variable network connectivity and integrate-and-fire dynamics. Starting from random initial conditions, we see the emergence of three broad classes of behaviors that differ in their collective spiking statistics. In the first class ("temporally-irregular"), all nodes have variable inter-spike intervals, and the resulting firing patterns are irregular. In the second ("temporally-regular"), the network generates a coherent, repeating pattern of activity in which all nodes fire with the same constant inter-spike interval. In the third ("chimeric"), subgroups of coherently-firing nodes coexist with temporally-irregular nodes. Chimera states have previously been observed in networks of oscillators; here, we find that the notions of temporally-regular and chimeric states encompass a much richer set of dynamical patterns than has yet been described. We also find that degree heterogeneity and connection density have a strong effect on the resulting state: in binomial random networks, high degree variance and intermediate connection density tend to produce temporally-irregular dynamics, while low degree variance and high connection density tend to produce temporally-regular dynamics. Chimera states arise with more frequency in networks with intermediate degree variance and either high or low connection densities. Finally, we demonstrate that a normalized compression distance, computed via the Lempel-Ziv complexity of nodal spike trains, can be used to distinguish these three classes of behavior even when the phase relationship between nodes is arbitrary.