Filter
Associated Lab
- Druckmann Lab (1) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (2) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (1) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Remove Jayaraman Lab filter Jayaraman Lab
- Looger Lab (1) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (1) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Romani Lab (1) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (1) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (1) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (1) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (1) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (1) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Associated Support Team
- Fly Facility (2) Apply Fly Facility filter
- Remove Janelia Experimental Technology filter Janelia Experimental Technology
- Project Technical Resources (1) Apply Project Technical Resources filter
- Scientific Computing Software (2) Apply Scientific Computing Software filter
- Scientific Computing Systems (1) Apply Scientific Computing Systems filter
6 Janelia Publications
Showing 1-6 of 6 resultsInternal representations are thought to support the generation of flexible, long-timescale behavioral patterns in both animals and artificial agents. Here, we present a novel conceptual framework for how Drosophila use their internal representation of head direction to maintain preferred headings in their surroundings, and how they learn to modify these preferences in the presence of selective thermal reinforcement. To develop the framework, we analyzed flies’ behavior in a classical operant visual learning paradigm and found that they use stochastically generated fixations and directed turns to express their heading preferences. Symmetries in the visual scene used in the paradigm allowed us to expose how flies’ probabilistic behavior in this setting is tethered to their head direction representation. We describe how flies’ ability to quickly adapt their behavior to the rules of their environment may rest on a behavioral policy whose parameters are flexible but whose form is genetically encoded in the structure of their circuits. Many of the mechanisms we outline may also be relevant for rapidly adaptive behavior driven by internal representations in other animals, including mammals.
The neural circuits responsible for animal behavior remain largely unknown. We summarize new methods and present the circuitry of a large fraction of the brain of the fruit fly . Improved methods include new procedures to prepare, image, align, segment, find synapses in, and proofread such large data sets. We define cell types, refine computational compartments, and provide an exhaustive atlas of cell examples and types, many of them novel. We provide detailed circuits consisting of neurons and their chemical synapses for most of the central brain. We make the data public and simplify access, reducing the effort needed to answer circuit questions, and provide procedures linking the neurons defined by our analysis with genetic reagents. Biologically, we examine distributions of connection strengths, neural motifs on different scales, electrical consequences of compartmentalization, and evidence that maximizing packing density is an important criterion in the evolution of the fly's brain.
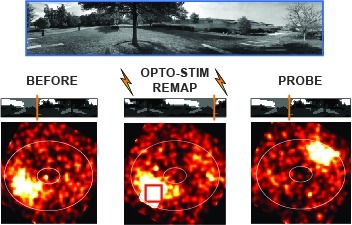
Many animals rely on an internal heading representation when navigating in varied environments. How this representation is linked to the sensory cues that define different surroundings is unclear. In the fly brain, heading is represented by 'compass' neurons that innervate a ring-shaped structure known as the ellipsoid body. Each compass neuron receives inputs from 'ring' neurons that are selective for particular visual features; this combination provides an ideal substrate for the extraction of directional information from a visual scene. Here we combine two-photon calcium imaging and optogenetics in tethered flying flies with circuit modelling, and show how the correlated activity of compass and visual neurons drives plasticity, which flexibly transforms two-dimensional visual cues into a stable heading representation. We also describe how this plasticity enables the fly to convert a partial heading representation, established from orienting within part of a novel setting, into a complete heading representation. Our results provide mechanistic insight into the memory-related computations that are essential for flexible navigation in varied surroundings.
Calcium imaging with genetically encoded calcium indicators (GECIs) is routinely used to measure neural activity in intact nervous systems. GECIs are frequently used in one of two different modes: to track activity in large populations of neuronal cell bodies, or to follow dynamics in subcellular compartments such as axons, dendrites and individual synaptic compartments. Despite major advances, calcium imaging is still limited by the biophysical properties of existing GECIs, including affinity, signal-to-noise ratio, rise and decay kinetics, and dynamic range. Using structure-guided mutagenesis and neuron-based screening, we optimized the green fluorescent protein-based GECI GCaMP6 for different modes of in vivo imaging. The jGCaMP7 sensors provide improved detection of individual spikes (jGCaMP7s,f), imaging in neurites and neuropil (jGCaMP7b), and tracking large populations of neurons using 2-photon (jGCaMP7s,f) or wide-field (jGCaMP7c) imaging.
Behavioral strategies employed for chemotaxis have been described across phyla, but the sensorimotor basis of this phenomenon has seldom been studied in naturalistic contexts. Here, we examine how signals experienced during free olfactory behaviors are processed by first-order olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) of the Drosophila larva. We find that OSNs can act as differentiators that transiently normalize stimulus intensity-a property potentially derived from a combination of integral feedback and feed-forward regulation of olfactory transduction. In olfactory virtual reality experiments, we report that high activity levels of the OSN suppress turning, whereas low activity levels facilitate turning. Using a generalized linear model, we explain how peripheral encoding of olfactory stimuli modulates the probability of switching from a run to a turn. Our work clarifies the link between computations carried out at the sensory periphery and action selection underlying navigation in odor gradients.
Drosophila melanogaster is a model organism rich in genetic tools to manipulate and identify neural circuits involved in specific behaviors. Here we present a technique for two-photon calcium imaging in the central brain of head-fixed Drosophila walking on an air-supported ball. The ball’s motion is tracked at high resolution and can be treated as a proxy for the fly’s own movements. We used the genetically encoded calcium sensor, GCaMP3.0, to record from important elements of the motion-processing pathway, the horizontal-system lobula plate tangential cells (LPTCs) in the fly optic lobe. We presented motion stimuli to the tethered fly and found that calcium transients in horizontal-system neurons correlated with robust optomotor behavior during walking. Our technique allows both behavior and physiology in identified neurons to be monitored in a genetic model organism with an extensive repertoire of walking behaviors.