Filter
Associated Lab
- Lavis Lab (1) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Remove Looger Lab filter Looger Lab
- Remove Sternson Lab filter Sternson Lab
2 Janelia Publications
Showing 1-2 of 2 resultsSmall molecules are important tools to measure and modulate intracellular signaling pathways. A longstanding limitation for using chemical compounds in complex tissues has been the inability to target bioactive small molecules to a specific cell class. Here, we describe a generalizable esterase-ester pair capable of targeted delivery of small molecules to living cells and tissue with cellular specificity. We used fluorogenic molecules to rapidly identify a small ester masking motif that is stable to endogenous esterases, but is efficiently removed by an exogenous esterase. This strategy allows facile targeting of dyes and drugs in complex biological environments to label specific cell types, illuminate gap junction connectivity, and pharmacologically perturb distinct subsets of cells. We expect this approach to have general utility for the specific delivery of many small molecules to defined cellular populations.
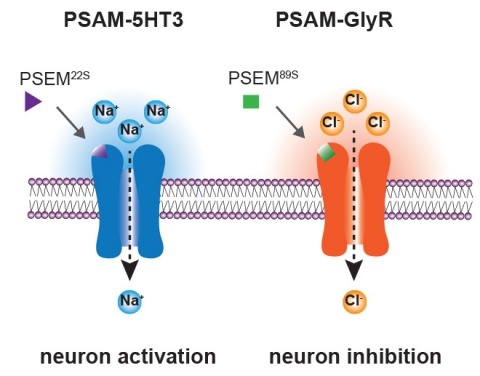
Ionic flux mediates essential physiological and behavioral functions in defined cell populations. Cell type-specific activators of diverse ionic conductances are needed for probing these effects. We combined chemistry and protein engineering to enable the systematic creation of a toolbox of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) with orthogonal pharmacologic selectivity and divergent functional properties. The LGICs and their small-molecule effectors were able to activate a range of ionic conductances in genetically specified cell types. LGICs constructed for neuronal perturbation could be used to selectively manipulate neuron activity in mammalian brains in vivo. The diversity of ion channel tools accessible from this approach will be useful for examining the relationship between neuronal activity and animal behavior, as well as for cell biological and physiological applications requiring chemical control of ion conductance.