Filter
Associated Lab
- Ahrens Lab (3) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (1) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Harris Lab (4) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (1) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (7) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (1) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (1) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (1) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Looger Lab (13) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (3) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (1) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Remove Schreiter Lab filter Schreiter Lab
- Svoboda Lab (9) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (1) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Turner Lab (2) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (1) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Publication Date
Type of Publication
- Remove Janelia filter Janelia
20 Publications
Showing 1-10 of 20 resultsGenetically encoded voltage indicators (GEVIs) allow optical recording of membrane potential from targeted cells in vivo. However, red GEVIs that are compatible with two-photon microscopy and that can be multiplexed in vivo with green reporters like GCaMP, are currently lacking. To address this gap, we explored diverse rhodopsin proteins as GEVIs and engineered a novel GEVI, 2Photron, based on a rhodopsin from the green algae Klebsormidium nitens. 2Photron, combined with two photon ultrafast local volume excitation (ULoVE), enabled multiplexed readout of spiking and subthreshold voltage simultaneously with GCaMP calcium signals in visual cortical neurons of awake, behaving mice. These recordings revealed the cell-specific relationship of spiking and subthreshold voltage dynamics with GCaMP responses, highlighting the challenges of extracting underlying spike trains from calcium imaging.
The fluorescent glutamate indicator iGluSnFR enables imaging of neurotransmission with genetic and molecular specificity. However, existing iGluSnFR variants exhibit low in vivo signal-to-noise ratios, saturating activation kinetics and exclusion from postsynaptic densities. Using a multiassay screen in bacteria, soluble protein and cultured neurons, we generated variants with improved signal-to-noise ratios and kinetics. We developed surface display constructs that improve iGluSnFR's nanoscopic localization to postsynapses. The resulting indicator iGluSnFR3 exhibits rapid nonsaturating activation kinetics and reports synaptic glutamate release with decreased saturation and increased specificity versus extrasynaptic signals in cultured neurons. Simultaneous imaging and electrophysiology at individual boutons in mouse visual cortex showed that iGluSnFR3 transients report single action potentials with high specificity. In vibrissal sensory cortex layer 4, we used iGluSnFR3 to characterize distinct patterns of touch-evoked feedforward input from thalamocortical boutons and both feedforward and recurrent input onto L4 cortical neuron dendritic spines.
The ability to optically image cellular transmembrane voltages at millisecond-timescale resolutions can offer unprecedented insight into the function of living brains in behaving animals. Here, we present a point mutation that increases the sensitivity of Ace2 opsin-based voltage indicators. We use the mutation to develop Voltron2, an improved chemigeneic voltage indicator that has a 65% higher sensitivity to single APs and 3-fold higher sensitivity to subthreshold potentials than Voltron. Voltron2 retained the sub-millisecond kinetics and photostability of its predecessor, although with lower baseline fluorescence. In multiple in vitro and in vivo comparisons with its predecessor across multiple species, we found Voltron2 to be more sensitive to APs and subthreshold fluctuations. Finally, we used Voltron2 to study and evaluate the possible mechanisms of interneuron synchronization in the mouse hippocampus. Overall, we have discovered a generalizable mutation that significantly increases the sensitivity of Ace2 rhodopsin-based sensors, improving their voltage reporting capability.
Calcium imaging with protein-based indicators is widely used to follow neural activity in intact nervous systems, but current protein sensors report neural activity at timescales much slower than electrical signalling and are limited by trade-offs between sensitivity and kinetics. Here we used large-scale screening and structure-guided mutagenesis to develop and optimize several fast and sensitive GCaMP-type indicators. The resulting 'jGCaMP8' sensors, based on the calcium-binding protein calmodulin and a fragment of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, have ultra-fast kinetics (half-rise times of 2 ms) and the highest sensitivity for neural activity reported for a protein-based calcium sensor. jGCaMP8 sensors will allow tracking of large populations of neurons on timescales relevant to neural computation.
We engineered electrochromic fluorescence resonance energy transfer (eFRET) genetically encoded voltage indicators (GEVIs) with “positive-going” fluorescence response to membrane depolarization through rational manipulation of the native proton transport pathway in microbial rhodopsins. We transformed the state-of-the-art eFRET GEVI Voltron into Positron, with kinetics and sensitivity equivalent to Voltron but flipped fluorescence signal polarity. We further applied this general approach to GEVIs containing different voltage sensitive rhodopsin domains and various fluorescent dye and fluorescent protein reporters.
Femtosecond lasers at fixed wavelengths above 1,000 nm are powerful, stable and inexpensive, making them promising sources for two-photon microscopy. Biosensors optimized for these wavelengths are needed for both next-generation microscopes and affordable turn-key systems. Here we report jYCaMP1, a yellow variant of the calcium indicator jGCaMP7 that outperforms its parent in mice and flies at excitation wavelengths above 1,000 nm and enables improved two-color calcium imaging with red fluorescent protein-based indicators.
Marking functionally distinct neuronal ensembles with high spatiotemporal resolution is a key challenge in systems neuroscience. We recently introduced CaMPARI, an engineered fluorescent protein whose green-to-red photoconversion depends on simultaneous light exposure and elevated calcium, which enabled marking active neuronal populations with single-cell and subsecond resolution. However, CaMPARI (CaMPARI1) has several drawbacks, including background photoconversion in low calcium, slow kinetics and reduced fluorescence after chemical fixation. In this work, we develop CaMPARI2, an improved sensor with brighter green and red fluorescence, faster calcium unbinding kinetics and decreased photoconversion in low calcium conditions. We demonstrate the improved performance of CaMPARI2 in mammalian neurons and in vivo in larval zebrafish brain and mouse visual cortex. Additionally, we herein develop an immunohistochemical detection method for specific labeling of the photoconverted red form of CaMPARI. The anti-CaMPARI-red antibody provides strong labeling that is selective for photoconverted CaMPARI in activated neurons in rodent brain tissue.
Calcium imaging with genetically encoded calcium indicators (GECIs) is routinely used to measure neural activity in intact nervous systems. GECIs are frequently used in one of two different modes: to track activity in large populations of neuronal cell bodies, or to follow dynamics in subcellular compartments such as axons, dendrites and individual synaptic compartments. Despite major advances, calcium imaging is still limited by the biophysical properties of existing GECIs, including affinity, signal-to-noise ratio, rise and decay kinetics, and dynamic range. Using structure-guided mutagenesis and neuron-based screening, we optimized the green fluorescent protein-based GECI GCaMP6 for different modes of in vivo imaging. The jGCaMP7 sensors provide improved detection of individual spikes (jGCaMP7s,f), imaging in neurites and neuropil (jGCaMP7b), and tracking large populations of neurons using 2-photon (jGCaMP7s,f) or wide-field (jGCaMP7c) imaging.
BACKGROUND: Genetically encoded calcium ion (Ca2+) indicators (GECIs) are indispensable tools for measuring Ca2+ dynamics and neuronal activities in vitro and in vivo. Red fluorescent protein (RFP)-based GECIs have inherent advantages relative to green fluorescent protein-based GECIs due to the longer wavelength light used for excitation. Longer wavelength light is associated with decreased phototoxicity and deeper penetration through tissue. Red GECI can also enable multicolor visualization with blue- or cyan-excitable fluorophores. RESULTS: Here we report the development, structure, and validation of a new RFP-based GECI, K-GECO1, based on a circularly permutated RFP derived from the sea anemone Entacmaea quadricolor. We have characterized the performance of K-GECO1 in cultured HeLa cells, dissociated neurons, stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes, organotypic brain slices, zebrafish spinal cord in vivo, and mouse brain in vivo. CONCLUSION: K-GECO1 is the archetype of a new lineage of GECIs based on the RFP eqFP578 scaffold. It offers high sensitivity and fast kinetics, similar or better than those of current state-of-the-art indicators, with diminished lysosomal accumulation and minimal blue-light photoactivation. Further refinements of the K-GECO1 lineage could lead to further improved variants with overall performance that exceeds that of the most highly optimized red GECIs.
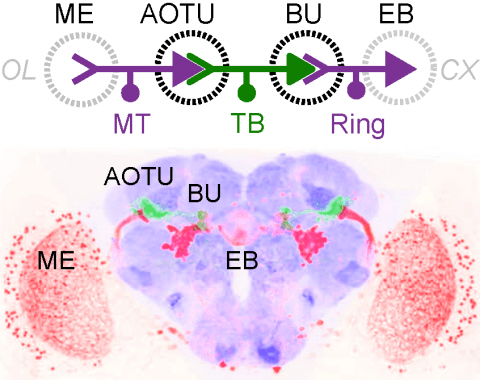
Many animals orient using visual cues, but how a single cue is selected from among many is poorly understood. Here we show that Drosophila ring neurons—central brain neurons implicated in navigation—display visual stimulus selection. Using in vivo two-color two-photon imaging with genetically encoded calcium indicators, we demonstrate that individual ring neurons inherit simple-cell-like receptive fields from their upstream partners. Stimuli in the contralateral visual field suppressed responses to ipsilateral stimuli in both populations. Suppression strength depended on when and where the contralateral stimulus was presented, an effect stronger in ring neurons than in their upstream inputs. This history-dependent effect on the temporal structure of visual responses, which was well modeled by a simple biphasic filter, may determine how visual references are selected for the fly's internal compass. Our approach highlights how two-color calcium imaging can help identify and localize the origins of sensory transformations across synaptically connected neural populations.