Filter
Associated Lab
- Remove Ahrens Lab filter Ahrens Lab
- Aso Lab (1) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Branson Lab (1) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (1) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (5) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Harris Lab (2) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (2) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (1) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Keller Lab (5) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (2) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (1) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (7) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (1) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (3) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (4) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (1) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (4) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (2) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (2) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (1) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (1) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Associated Support Team
Publication Date
- 2024 (5) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (4) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (4) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (2) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (4) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (5) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (4) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (2) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (7) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (3) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (3) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (2) Apply 2013 filter
45 Janelia Publications
Showing 21-30 of 45 resultsAll multicellular systems produce and dynamically regulate extracellular matrices (ECM) that play important roles in both biochemical and mechanical signaling. Though the spatial arrangement of these extracellular assemblies is critical to their biological functions, visualization of ECM structure is challenging, in part because the biomolecules that compose the ECM are difficult to fluorescently label individually and collectively. Here, we present a cell-impermeable small molecule fluorophore, termed Rhobo6, that turns on and red shifts upon reversible binding to glycans. Given that most ECM components are densely glycosylated, the dye enables wash-free visualization of ECM, in systems ranging from in vitro substrates to in vivo mouse mammary tumors. Relative to existing techniques, Rhobo6 provides a broad substrate profile, superior tissue penetration, nonperturbative labeling, and negligible photobleaching. This work establishes a straightforward method for imaging the distribution of ECM in live tissues and organisms, lowering barriers for investigation of extracellular biology.
Due to their small size and transparency, zebrafish larvae are amenable to a range of fluorescence microscopy techniques. With the development of sensitive genetically encoded calcium indicators, this has extended to the whole-brain imaging of neural activity with cellular resolution. This technique has been used to study brain-wide population dynamics accompanying sensory processing and sensorimotor transformations, and has spurred the development of innovative closed-loop behavioral paradigms in which stimulus-response relationships can be studied. More recently, microscopes have been developed that allow whole-brain calcium imaging in freely swimming and behaving larvae. In this review, we highlight the technologies underlying whole-brain functional imaging in zebrafish, provide examples of the sensory and motor processes that have been studied with this technique, and discuss the need to merge data from whole-brain functional imaging studies with neurochemical and anatomical information to develop holistic models of functional neural circuits.
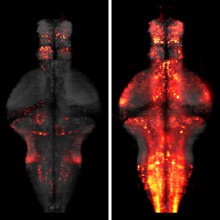
Mood-altering compounds hold promise for the treatment of many psychiatric disorders, such as depression, but connecting their molecular, circuit, and behavioral effects has been challenging. Here we find that, analogous to effects in rodent learned helplessness models, ketamine pre-exposure persistently suppresses futility-induced passivity in larval zebrafish. While antidepressants are thought to primarily act on neurons, brain-wide imaging in behaving zebrafish showed that ketamine elevates intracellular calcium in astroglia for many minutes, followed by persistent calcium downregulation post-washout. Calcium elevation depends on astroglial α1-adrenergic receptors and is required for suppression of passivity. Chemo-/optogenetic perturbations of noradrenergic neurons and astroglia demonstrate that the aftereffects of glial calcium elevation are sufficient to suppress passivity by inhibiting neuronal-astroglial integration of behavioral futility. Imaging in mouse cortex reveals that ketamine elevates astroglial calcium through conserved pathways, suggesting that ketamine exerts its behavioral effects by persistently modulating evolutionarily ancient neuromodulatory systems spanning neurons and astroglia.
The identification of active neurons and circuits in vivo is a fundamental challenge in understanding the neural basis of behavior. Genetically encoded calcium (Ca(2+)) indicators (GECIs) enable quantitative monitoring of cellular-resolution activity during behavior. However, such indicators require online monitoring within a limited field of view. Alternatively, post hoc staining of immediate early genes (IEGs) indicates highly active cells within the entire brain, albeit with poor temporal resolution. We designed a fluorescent sensor, CaMPARI, that combines the genetic targetability and quantitative link to neural activity of GECIs with the permanent, large-scale labeling of IEGs, allowing a temporally precise "activity snapshot" of a large tissue volume. CaMPARI undergoes efficient and irreversible green-to-red conversion only when elevated intracellular Ca(2+) and experimenter-controlled illumination coincide. We demonstrate the utility of CaMPARI in freely moving larvae of zebrafish and flies, and in head-fixed mice and adult flies.
The dense connectivity in the brain means that one neuron's activity can influence many others. To observe this interconnected system comprehensively, an aspiration within neuroscience is to record from as many neurons as possible at the same time. There are two useful routes toward this goal: one is to expand the spatial extent of functional imaging techniques, and the second is to use animals with small brains. Here we review recent progress toward imaging many neurons and complete populations of identified neurons in small vertebrates and invertebrates.
The processing of sensory input and the generation of behavior involves large networks of neurons, which necessitates new technology for recording from many neurons in behaving animals. In the larval zebrafish, light-sheet microscopy can be used to record the activity of almost all neurons in the brain simultaneously at single-cell resolution. Existing implementations, however, cannot be combined with visually driven behavior because the light sheet scans over the eye, interfering with presentation of controlled visual stimuli. Here we describe a system that overcomes the confounding eye stimulation through the use of two light sheets and combines whole-brain light-sheet imaging with virtual reality for fictively behaving larval zebrafish.
Developments in electrical and optical recording technology are scaling up the size of neuronal populations that can be monitored simultaneously. Light-sheet imaging is rapidly gaining traction as a method for optically interrogating activity in large networks and presents both opportunities and challenges for understanding circuit function.
Understanding brain function requires monitoring and interpreting the activity of large networks of neurons during behavior. Advances in recording technology are greatly increasing the size and complexity of neural data. Analyzing such data will pose a fundamental bottleneck for neuroscience. We present a library of analytical tools called Thunder built on the open-source Apache Spark platform for large-scale distributed computing. The library implements a variety of univariate and multivariate analyses with a modular, extendable structure well-suited to interactive exploration and analysis development. We demonstrate how these analyses find structure in large-scale neural data, including whole-brain light-sheet imaging data from fictively behaving larval zebrafish, and two-photon imaging data from behaving mouse. The analyses relate neuronal responses to sensory input and behavior, run in minutes or less and can be used on a private cluster or in the cloud. Our open-source framework thus holds promise for turning brain activity mapping efforts into biological insights.
Motor neurons are the final common pathway through which the brain controls movement of the body, forming the basic elements from which all movement is composed. Yet how a single motor neuron contributes to control during natural movement remains unclear. Here we anatomically and functionally characterize the individual roles of the motor neurons that control head movement in the fly, Drosophila melanogaster. Counterintuitively, we find that activity in a single motor neuron rotates the head in different directions, depending on the starting posture of the head, such that the head converges towards a pose determined by the identity of the stimulated motor neuron. A feedback model predicts that this convergent behaviour results from motor neuron drive interacting with proprioceptive feedback. We identify and genetically suppress a single class of proprioceptive neuron that changes the motor neuron-induced convergence as predicted by the feedback model. These data suggest a framework for how the brain controls movements: instead of directly generating movement in a given direction by activating a fixed set of motor neurons, the brain controls movements by adding bias to a continuing proprioceptive-motor loop.
Progress in modern neuroscience critically depends on our ability to observe the activity of large neuronal populations with cellular spatial and high temporal resolution. However, two bottlenecks constrain efforts towards fast imaging of large populations. First, the resulting large video data is challenging to analyze. Second, there is an explicit tradeoff between imaging speed, signal-to-noise, and field of view: with current recording technology we cannot image very large neuronal populations with simultaneously high spatial and temporal resolution. Here we describe multi-scale approaches for alleviating both of these bottlenecks. First, we show that spatial and temporal decimation techniques based on simple local averaging provide order-of-magnitude speedups in spatiotemporally demixing calcium video data into estimates of single-cell neural activity. Second, once the shapes of individual neurons have been identified at fine scale (e.g., after an initial phase of conventional imaging with standard temporal and spatial resolution), we find that the spatial/temporal resolution tradeoff shifts dramatically: after demixing we can accurately recover denoised fluorescence traces and deconvolved neural activity of each individual neuron from coarse scale data that has been spatially decimated by an order of magnitude. This offers a cheap method for compressing this large video data, and also implies that it is possible to either speed up imaging significantly, or to "zoom out" by a corresponding factor to image order-of-magnitude larger neuronal populations with minimal loss in accuracy or temporal resolution.