Filter
Associated Lab
- Ahrens Lab (3) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (3) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (5) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (8) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Branson Lab (6) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (1) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (1) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (2) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Cui Lab (2) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (5) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (1) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (4) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (3) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (1) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (1) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (3) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (10) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (3) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (2) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (1) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hess Lab (5) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (1) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (3) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (1) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keller Lab (7) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (7) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (4) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (4) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (4) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (11) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (1) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (3) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (1) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (2) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (4) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (8) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (1) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (7) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (2) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (4) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (1) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (6) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (5) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (7) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (1) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (4) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (1) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Wu Lab (2) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (1) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (1) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Associated Support Team
Publication Date
- December 2014 (31) Apply December 2014 filter
- November 2014 (7) Apply November 2014 filter
- October 2014 (14) Apply October 2014 filter
- September 2014 (14) Apply September 2014 filter
- August 2014 (11) Apply August 2014 filter
- July 2014 (23) Apply July 2014 filter
- June 2014 (13) Apply June 2014 filter
- May 2014 (10) Apply May 2014 filter
- April 2014 (18) Apply April 2014 filter
- March 2014 (13) Apply March 2014 filter
- February 2014 (11) Apply February 2014 filter
- January 2014 (25) Apply January 2014 filter
- Remove 2014 filter 2014
190 Janelia Publications
Showing 151-160 of 190 resultsStaphylococcus aureus responds to changing extracellular environments in part by adjusting its proteome through alterations of transcriptional priorities and selective degradation of the preexisting pool of proteins. In Bacillus subtilis, the proteolytic adaptor protein MecA has been shown to play a role in assisting with the proteolytic degradation of proteins involved in competence and the oxidative stress response. However, the targets of TrfA, the MecA homolog in S. aureus, have not been well characterized. In this work, we investigated how TrfA assists chaperones and proteases to regulate the proteolysis of several classes of proteins in S. aureus. By fusing the last 3 amino acids of the SsrA degradation tag to Venus, a rapidly folding yellow fluorescent protein, we obtained both fluorescence-based and Western blot assay-based evidence that TrfA and ClpCP are the adaptor and protease, respectively, responsible for the degradation of the SsrA-tagged protein in S. aureus. Notably, the impact of TrfA on degradation was most prominent during late log phase and early stationary phase, due in part to a combination of transcriptional regulation and proteolytic degradation of TrfA by ClpCP. We also characterized the temporal transcriptional regulation governing TrfA activity, wherein Spx, a redox-sensitive transcriptional regulator degraded by ClpXP, activates trfA transcription while repressing its own promoter. Finally, the scope of TrfA-mediated proteolysis was expanded by identifying TrfA as the adaptor that works with ClpCP to degrade antitoxins in S. aureus. Together, these results indicate that the adaptor TrfA adds temporal nuance to protein degradation by ClpCP in S. aureus.
The generation of four-dimensional (4D) confocal datasets; consisting of 3D image sequences over time; provides an excellent methodology to capture cellular behaviors involved in developmental processes. The ability to track and follow cell movements is limited by sample movements that occur due to drift of the sample or, in some cases, growth during image acquisition. Tracking cells in datasets affected by drift and/or growth will incorporate these movements into any analysis of cell position. This may result in the apparent movement of static structures within the sample. Therefore prior to cell tracking, any sample drift should be corrected. Using the open source Fiji distribution (1) of ImageJ (2,3) and the incorporated LOCI tools (4), we developed the Correct 3D drift plug-in to remove erroneous sample movement in confocal datasets. This protocol effectively compensates for sample translation or alterations in focal position by utilizing phase correlation to register each time-point of a four-dimensional confocal datasets while maintaining the ability to visualize and measure cell movements over extended time-lapse experiments.
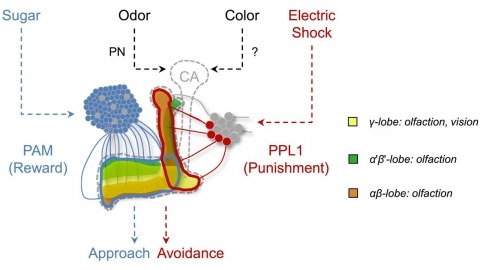
In nature, animals form memories associating reward or punishment with stimuli from different sensory modalities, such as smells and colors. It is unclear, however, how distinct sensory memories are processed in the brain. We established appetitive and aversive visual learning assays for Drosophila that are comparable to the widely used olfactory learning assays. These assays share critical features, such as reinforcing stimuli (sugar reward and electric shock punishment), and allow direct comparison of the cellular requirements for visual and olfactory memories. We found that the same subsets of dopamine neurons drive formation of both sensory memories. Furthermore, distinct yet partially overlapping subsets of mushroom body intrinsic neurons are required for visual and olfactory memories. Thus, our results suggest that distinct sensory memories are processed in a common brain center. Such centralization of related brain functions is an economical design that avoids the repetition of similar circuit motifs.
Enhancer-binding pluripotency regulators (Sox2 and Oct4) play a seminal role in embryonic stem (ES) cell-specific gene regulation. Here, we combine in vivo and in vitro single-molecule imaging, transcription factor (TF) mutagenesis, and ChIP-exo mapping to determine how TFs dynamically search for and assemble on their cognate DNA target sites. We find that enhanceosome assembly is hierarchically ordered with kinetically favored Sox2 engaging the target DNA first, followed by assisted binding of Oct4. Sox2/Oct4 follow a trial-and-error sampling mechanism involving 84-97 events of 3D diffusion (3.3-3.7 s) interspersed with brief nonspecific collisions (0.75-0.9 s) before acquiring and dwelling at specific target DNA (12.0-14.6 s). Sox2 employs a 3D diffusion-dominated search mode facilitated by 1D sliding along open DNA to efficiently locate targets. Our findings also reveal fundamental aspects of gene and developmental regulation by fine-tuning TF dynamics and influence of the epigenome on target search parameters.
Gene regulation relies on transcription factors (TFs) exploring the nucleus searching their targets. So far, most studies have focused on how fast TFs diffuse, underestimating the role of nuclear architecture. We implemented a single-molecule tracking assay to determine TFs dynamics. We found that c-Myc is a global explorer of the nucleus. In contrast, the positive transcription elongation factor P-TEFb is a local explorer that oversamples its environment. Consequently, each c-Myc molecule is equally available for all nuclear sites while P-TEFb reaches its targets in a position-dependent manner. Our observations are consistent with a model in which the exploration geometry of TFs is restrained by their interactions with nuclear structures and not by exclusion. The geometry-controlled kinetics of TFs target-search illustrates the influence of nuclear architecture on gene regulation, and has strong implications on how proteins react in the nucleus and how their function can be regulated in space and time.
Transcription is an inherently stochastic, noisy, and multi-step process, in which fluctuations at every step can cause variations in RNA synthesis, and affect physiology and differentiation decisions in otherwise identical cells. However, it has been an experimental challenge to directly link the stochastic events at the promoter to transcript production. Here we established a fast fluorescence in situ hybridization (fastFISH) method that takes advantage of intrinsically unstructured nucleic acid sequences to achieve exceptionally fast rates of specific hybridization (\~{}10e7 M(-1)s(-1)), and allows deterministic detection of single nascent transcripts. Using a prototypical RNA polymerase, we demonstrated the use of fastFISH to measure the kinetic rates of promoter escape, elongation, and termination in one assay at the single-molecule level, at sub-second temporal resolution. The principles of fastFISH design can be used to study stochasticity in gene regulation, to select targets for gene silencing, and to design nucleic acid nanostructures. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01775.001.
BACKGROUND: Logos are commonly used in molecular biology to provide a compact graphical representation of the conservation pattern of a set of sequences. They render the information contained in sequence alignments or profile hidden Markov models by drawing a stack of letters for each position, where the height of the stack corresponds to the conservation at that position, and the height of each letter within a stack depends on the frequency of that letter at that position. RESULTS: We present a new tool and web server, called Skylign, which provides a unified framework for creating logos for both sequence alignments and profile hidden Markov models. In addition to static image files, Skylign creates a novel interactive logo plot for inclusion in web pages. These interactive logos enable scrolling, zooming, and inspection of underlying values. Skylign can avoid sampling bias in sequence alignments by down-weighting redundant sequences and by combining observed counts with informed priors. It also simplifies the representation of gap parameters, and can optionally scale letter heights based on alternate calculations of the conservation of a position. CONCLUSION: Skylign is available as a website, a scriptable web service with a RESTful interface, and as a software package for download. Skylign’s interactive logos are easily incorporated into a web page with just a few lines of HTML markup. Skylign may be found at http://skylign.org.
Pixel and superpixel classifiers have become essential tools for EM segmentation algorithms. Training these classifiers remains a major bottleneck primarily due to the requirement of completely annotating the dataset which is tedious, error-prone and costly. In this paper, we propose an interactive learning scheme for the superpixel classifier for EM segmentation. Our algorithm is "active semi-supervised" because it requests the labels of a small number of examples from user and applies label propagation technique to generate these queries. Using only a small set (<20%) of all datapoints, the proposed algorithm consistently generates a classifier almost as accurate as that estimated from a complete groundtruth. We provide segmentation results on multiple datasets to show the strength of these classifiers.
Pixel and superpixel classifiers have become essential tools for EM segmentation algorithms. Training these classifiers remains a major bottleneck primarily due to the requirement of completely annotating the dataset which is tedious, error-prone and costly. In this paper, we propose an interactive learning scheme for the superpixel classifier for EM segmentation. Our algorithm is 'active semi-supervised' because it requests the labels of a small number of examples from user and applies label propagation technique to generate these queries. Using only a small set (< 20%) of all datapoints, the proposed algorithm consistently generates a classifier almost as accurate as that estimated from a complete groundtruth. We provide segmentation results on multiple datasets to show the strength of these classifiers.
We propose a version of least-mean-square (LMS) algorithm for sparse system identification. Our algorithm called online linearized Bregman iteration (OLBI) is derived from minimizing the cumulative prediction error squared along with an l 1 -l 2 norm regularizer. By systematically treating the non-differentiable regularizer we arrive at a simple two-step iteration. We demonstrate that OLBI is bias free and compare its operation with existing sparse LMS algorithms by rederiving them in the online convex optimization framework. We perform convergence analysis of OLBI for white input signals and derive theoretical expressions for the steady state mean square deviations (MSD). We demonstrate numerically that OLBI improves the performance of LMS type algorithms for signals generated from sparse tap weights.