Filter
Associated Lab
- Aso Lab (29) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (1) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Bock Lab (2) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (7) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (5) Apply Card Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (1) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (2) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (1) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (1) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Funke Lab (1) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Harris Lab (3) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (1) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (2) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (5) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (5) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (1) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Looger Lab (2) Apply Looger Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (1) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (1) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (15) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (1) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (1) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Remove Rubin Lab filter Rubin Lab
- Saalfeld Lab (4) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (7) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (1) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (3) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (1) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (1) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (3) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Truman Lab (4) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (1) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (5) Apply Turner Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Associated Support Team
- Electron Microscopy (3) Apply Electron Microscopy filter
- Fly Facility (8) Apply Fly Facility filter
- Janelia Experimental Technology (1) Apply Janelia Experimental Technology filter
- Management Team (1) Apply Management Team filter
- Primary & iPS Cell Culture (1) Apply Primary & iPS Cell Culture filter
- Project Technical Resources (8) Apply Project Technical Resources filter
- Quantitative Genomics (2) Apply Quantitative Genomics filter
- Scientific Computing Software (9) Apply Scientific Computing Software filter
- Scientific Computing Systems (2) Apply Scientific Computing Systems filter
Publication Date
- 2024 (3) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (6) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (1) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (4) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (9) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (6) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (7) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (15) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (3) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (16) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (8) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (5) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (7) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (3) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (2) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (1) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (2) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (2) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (1) Apply 2006 filter
101 Janelia Publications
Showing 31-40 of 101 resultsVision provides animals with detailed information about their surroundings, conveying diverse features such as color, form, and movement across the visual scene. Computing these parallel spatial features requires a large and diverse network of neurons, such that in animals as distant as flies and humans, visual regions comprise half the brain’s volume. These visual brain regions often reveal remarkable structure-function relationships, with neurons organized along spatial maps with shapes that directly relate to their roles in visual processing. To unravel the stunning diversity of a complex visual system, a careful mapping of the neural architecture matched to tools for targeted exploration of that circuitry is essential. Here, we report a new connectome of the right optic lobe from a male Drosophila central nervous system FIB-SEM volume and a comprehensive inventory of the fly’s visual neurons. We developed a computational framework to quantify the anatomy of visual neurons, establishing a basis for interpreting how their shapes relate to spatial vision. By integrating this analysis with connectivity information, neurotransmitter identity, and expert curation, we classified the 53,000 neurons into 727 types, about half of which are systematically described and named for the first time. Finally, we share an extensive collection of split-GAL4 lines matched to our neuron type catalog. Together, this comprehensive set of tools and data unlock new possibilities for systematic investigations of vision in Drosophila, a foundation for a deeper understanding of sensory processing.
Many animals, including humans, navigate their surroundings by visual input, yet we understand little about how visual information is transformed and integrated by the navigation system. In , compass neurons in the donut-shaped ellipsoid body of the central complex generate a sense of direction by integrating visual input from ring neurons, a part of the anterior visual pathway (AVP). Here, we densely reconstruct all neurons in the AVP using FlyWire, an AI-assisted tool for analyzing electron-microscopy data. The AVP comprises four neuropils, sequentially linked by three major classes of neurons: MeTu neurons, which connect the medulla in the optic lobe to the small unit of anterior optic tubercle (AOTUsu) in the central brain; TuBu neurons, which connect the anterior optic tubercle to the bulb neuropil; and ring neurons, which connect the bulb to the ellipsoid body. Based on neuronal morphologies, connectivity between different neural classes, and the locations of synapses, we identified non-overlapping channels originating from four types of MeTu neurons, which we further divided into ten subtypes based on the presynaptic connections in medulla and postsynaptic connections in AOTUsu. To gain an objective measure of the natural variation within the pathway, we quantified the differences between anterior visual pathways from both hemispheres and between two electron-microscopy datasets. Furthermore, we infer potential visual features and the visual area from which any given ring neuron receives input by combining the connectivity of the entire AVP, the MeTu neurons' dendritic fields, and presynaptic connectivity in the optic lobes. These results provide a strong foundation for understanding how distinct visual features are extracted and transformed across multiple processing stages to provide critical information for computing the fly's sense of direction.
Motion detection is a fundamental neural computation performed by many sensory systems. In the fly, local motion computation is thought to occur within the first two layers of the visual system, the lamina and medulla. We constructed specific genetic driver lines for each of the 12 neuron classes in the lamina. We then depolarized and hyperpolarized each neuron type and quantified fly behavioral responses to a diverse set of motion stimuli. We found that only a small number of lamina output neurons are essential for motion detection, while most neurons serve to sculpt and enhance these feedforward pathways. Two classes of feedback neurons (C2 and C3), and lamina output neurons (L2 and L4), are required for normal detection of directional motion stimuli. Our results reveal a prominent role for feedback and lateral interactions in motion processing and demonstrate that motion-dependent behaviors rely on contributions from nearly all lamina neuron classes.
The Drosophila mushroom body (MB) is an associative learning network that is important for the control of sleep. We have recently identified particular intrinsic MB Kenyon cell (KC) classes that regulate sleep through synaptic activation of particular MB output neurons (MBONs) whose axons convey sleep control signals out of the MB to downstream target regions. Specifically, we found that sleep-promoting KCs increase sleep by preferentially activating cholinergic sleep-promoting MBONs, while wake-promoting KCs decrease sleep by preferentially activating glutamatergic wake-promoting MBONs. Here we use a combination of genetic and physiological approaches to identify wake-promoting dopaminergic neurons (DANs) that innervate the MB, and show that they activate wake-promoting MBONs. These studies reveal a dopaminergic sleep control mechanism that likely operates by modulation of KC-MBON microcircuits.
Optical and electron microscopy have made tremendous inroads toward understanding the complexity of the brain. However, optical microscopy offers insufficient resolution to reveal subcellular details, and electron microscopy lacks the throughput and molecular contrast to visualize specific molecular constituents over millimeter-scale or larger dimensions. We combined expansion microscopy and lattice light-sheet microscopy to image the nanoscale spatial relationships between proteins across the thickness of the mouse cortex or the entire Drosophila brain. These included synaptic proteins at dendritic spines, myelination along axons, and presynaptic densities at dopaminergic neurons in every fly brain region. The technology should enable statistically rich, large-scale studies of neural development, sexual dimorphism, degree of stereotypy, and structural correlations to behavior or neural activity, all with molecular contrast.
Previously, we identified that visual and olfactory associative memories of Drosophila share the mushroom body (MB) circuits (Vogt et al. 2014). Despite well-characterized odor representations in the Drosophila MB, the MB circuit for visual information is totally unknown. Here we show that a small subset of MB Kenyon cells (KCs) selectively responds to visual but not olfactory stimulation. The dendrites of these atypical KCs form a ventral accessory calyx (vAC), distinct from the main calyx that receives olfactory input. We identified two types of visual projection neurons (VPNs) directly connecting the optic lobes and the vAC. Strikingly, these VPNs are differentially required for visual memories of color and brightness. The segregation of visual and olfactory domains in the MB allows independent processing of distinct sensory memories and may be a conserved form of sensory representations among insects.
Visual motion perception is critical to many animal behaviors, and flies have emerged as a powerful model system for exploring this fundamental neural computation. Although numerous studies have suggested that fly motion vision is governed by a simple neural circuit [1-3], the implementation of this circuit has remained mysterious for decades. Connectomics and neurogenetics have produced a surge in recent progress, and several studies have shown selectivity for light increments (ON) or decrements (OFF) in key elements associated with this circuit [4-7]. However, related studies have reached disparate conclusions about where this selectivity emerges and whether it plays a major role in motion vision [8-13]. To address these questions, we examined activity in the neuropil thought to be responsible for visual motion detection, the medulla, of Drosophila melanogaster in response to a range of visual stimuli using two-photon calcium imaging. We confirmed that the input neurons of the medulla, the LMCs, are not responsible for light-on and light-off selectivity. We then examined the pan-neural response of medulla neurons and found prominent selectivity for light-on and light-off in layers of the medulla associated with two anatomically derived pathways (L1/L2 associated) [14, 15]. We next examined the activity of prominent interneurons within each pathway (Mi1 and Tm1) and found that these neurons have corresponding selectivity for light-on or light-off. These results provide direct evidence that motion is computed in parallel light-on and light-off pathways, demonstrate that this selectivity emerges in neurons immediately downstream of the LMCs, and specify where crucial elements of motion computation occur.
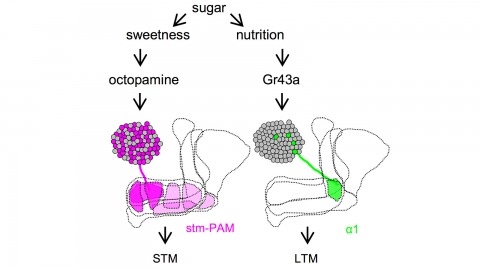
Drosophila melanogaster can acquire a stable appetitive olfactory memory when the presentation of a sugar reward and an odor are paired. However, the neuronal mechanisms by which a single training induces long-term memory are poorly understood. Here we show that two distinct subsets of dopamine neurons in the fly brain signal reward for short-term (STM) and long-term memories (LTM). One subset induces memory that decays within several hours, whereas the other induces memory that gradually develops after training. They convey reward signals to spatially segregated synaptic domains of the mushroom body (MB), a potential site for convergence. Furthermore, we identified a single type of dopamine neuron that conveys the reward signal to restricted subdomains of the mushroom body lobes and induces long-term memory. Constant appetitive memory retention after a single training session thus comprises two memory components triggered by distinct dopamine neurons.
Associative learning is thought to involve parallel and distributed mechanisms of memory formation and storage. In Drosophila, the mushroom body (MB) is the major site of associative odor memory formation. Previously we described the anatomy of the adult MB and defined 20 types of dopaminergic neurons (DANs) that each innervate distinct MB compartments (Aso et al., 2014a; Aso et al., 2014b). Here we compare the properties of memories formed by optogenetic activation of individual DAN cell types. We found extensive differences in training requirements for memory formation, decay dynamics, storage capacity and flexibility to learn new associations. Even a single DAN cell type can either write or reduce an aversive memory, or write an appetitive memory, depending on when it is activated relative to odor delivery. Our results show that different learning rules are executed in seemingly parallel memory systems, providing multiple distinct circuit-based strategies to predict future events from past experiences.
The mushroom body (MB) is the center for associative learning in insects. In Drosophila, intersectional split-GAL4 drivers and electron microscopy (EM) connectomes have laid the foundation for precise interrogation of the MB neural circuits. However, many cell types upstream and downstream of the MB remained to be investigated due to lack of driver lines. Here we describe a new collection of over 800 split-GAL4 and split-LexA drivers that cover approximately 300 cell types, including sugar sensory neurons, putative nociceptive ascending neurons, olfactory and thermo-/hygro-sensory projection neurons, interneurons connected with the MB-extrinsic neurons, and various other cell types. We characterized activation phenotypes for a subset of these lines and identified the sugar sensory neuron line most suitable for reward substitution. Leveraging the thousands of confocal microscopy images associated with the collection, we analyzed neuronal morphological stereotypy and discovered that one set of mushroom body output neurons, MBON08/MBON09, exhibits striking individuality and asymmetry across animals. In conjunction with the EM connectome maps, the driver lines reported here offer a powerful resource for functional dissection of neural circuits for associative learning in adult Drosophila.