Filter
Associated Lab
- Dudman Lab (1) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Harris Lab (7) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Hess Lab (1) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Remove Lee (Albert) Lab filter Lee (Albert) Lab
- Pachitariu Lab (2) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Romani Lab (1) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (1) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (1) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (3) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
Associated Support Team
Publication Date
29 Janelia Publications
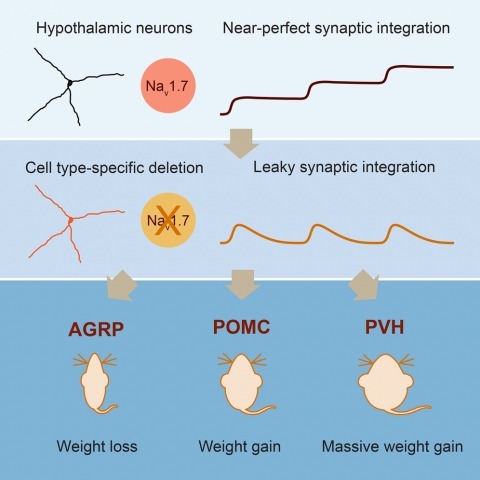
Showing 21-29 of 29 resultsNeurons are well suited for computations on millisecond timescales, but some neuronal circuits set behavioral states over long time periods, such as those involved in energy homeostasis. We found that multiple types of hypothalamic neurons, including those that oppositely regulate body weight, are specialized as near-perfect synaptic integrators that summate inputs over extended timescales. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are greatly prolonged, outlasting the neuronal membrane time-constant up to 10-fold. This is due to the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 (Scn9a), previously associated with pain-sensation but not synaptic integration. Scn9a deletion in AGRP, POMC, or paraventricular hypothalamic neurons reduced EPSP duration, synaptic integration, and altered body weight in mice. In vivo whole-cell recordings in the hypothalamus confirmed near-perfect synaptic integration. These experiments show that integration of synaptic inputs over time by Nav1.7 is critical for body weight regulation and reveal a mechanism for synaptic control of circuits regulating long term homeostatic functions.
Measuring the dynamics of neural processing across time scales requires following the spiking of thousands of individual neurons over milliseconds and months. To address this need, we introduce the Neuropixels 2.0 probe together with newly designed analysis algorithms. The probe has more than 5000 sites and is miniaturized to facilitate chronic implants in small mammals and recording during unrestrained behavior. High-quality recordings over long time scales were reliably obtained in mice and rats in six laboratories. Improved site density and arrangement combined with newly created data processing methods enable automatic post hoc correction for brain movements, allowing recording from the same neurons for more than 2 months. These probes and algorithms enable stable recordings from thousands of sites during free behavior, even in small animals such as mice.
Electrophysiology is one of the major experimental techniques used in neuroscience. The favorable spatial and temporal resolution as well as the increasingly larger site counts of brain recording electrodes contribute to the popularity and importance of electrophysiology in neuroscience. Such electrodes are typically mechanically placed in the brain to perform acute or chronic freely moving animal measurements. The micro positioners currently used for such tasks employ a single translator per independent probe being placed into the targeted brain region, leading to significant size and weight restrictions. To overcome this limitation, we have developed a miniature robotic multi-probe neural microdrive that utilizes novel phase-change-material-filled resistive heater micro-grippers. The microscopic dimensions, gentle gripping action, independent electronic actuation control, and high packing density of the grippers allow for micrometer-precision independent positioning of multiple arbitrarily shaped parallel neural electrodes with only a single piezo actuator in an inchworm motor configuration. This multi-probe-single-actuator design allows for significant size and weight reduction, as well as remote control and potential automation of the microdrive. We demonstrate accurate placement of multiple independent recording electrodes into the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus in vivo in acute and chronic settings. Thus, our robotic neural microdrive technology is applicable towards basic neuroscience and clinical studies, as well as other multi-probe or multi-sensor micro-positioning applications.
The claustrum is one of the most widely connected regions of the forebrain, yet its function has remained obscure, largely due to the experimentally challenging nature of targeting this small, thin, and elongated brain area. However, recent advances in molecular techniques have enabled the anatomy and physiology of the claustrum to be studied with the spatiotemporal and cell type-specific precision required to eventually converge on what this area does. Here we review early anatomical and electrophysiological results from cats and primates, as well as recent work in the rodent, identifying the connectivity, cell types, and physiological circuit mechanisms underlying the communication between the claustrum and the cortex. The emerging picture is one in which the rodent claustrum is closely tied to frontal/limbic regions and plays a role in processes, such as attention, that are associated with these areas. Expected final online publication date for the , Volume 43 is July 8, 2020. Please see http://www.annualreviews.org/page/journal/pubdates for revised estimates.
The claustrum is a brain region that has been investigated for over 200 years, yet its precise function remains unknown. In the final posthumously released article of Francis Crick, written with Christof Koch, the claustrum was suggested to be critically linked to consciousness. Though the claustrum remained relatively obscure throughout the last half century, it has enjoyed a renewed interest in the last 15 years since Crick and Koch's article. During this time, the claustrum, like many other brain regions, has been studied with the myriad of modern systems neuroscience tools that have been made available by the intersection of genetic and viral technologies. This has uncovered new information about its anatomical connectivity and physiological properties and begun to reveal aspects of its function. From these studies, one clear consensus has emerged which supports Crick and Koch's primary interest in the claustrum: the claustrum has widespread extensive connectivity with the entire cerebral cortex, suggesting a prominent role in 'higher order processes'.
Hippocampal activity represents many behaviorally important variables, including context, an animal's location within a given environmental context, time, and reward. Using longitudinal calcium imaging in mice, multiple large virtual environments, and differing reward contingencies, we derived a unified probabilistic model of CA1 representations centered on a single feature-the field propensity. Each cell's propensity governs how many place fields it has per unit space, predicts its reward-related activity, and is preserved across distinct environments and over months. Propensity is broadly distributed-with many low, and some very high, propensity cells-and thus strongly shapes hippocampal representations. This results in a range of spatial codes, from sparse to dense. Propensity varied ∼10-fold between adjacent cells in salt-and-pepper fashion, indicating substantial functional differences within a presumed cell type. Intracellular recordings linked propensity to cell excitability. The stability of each cell's propensity across conditions suggests this fundamental property has anatomical, transcriptional, and/or developmental origins.
The hippocampus is critical for recollecting and imagining experiences. This is believed to involve voluntarily drawing from hippocampal memory representations of people, events, and places, including maplike representations of familiar environments. However, whether representations in such "cognitive maps" can be volitionally accessed is unknown. We developed a brain-machine interface to test whether rats can do so by controlling their hippocampal activity in a flexible, goal-directed, and model-based manner. We found that rats can efficiently navigate or direct objects to arbitrary goal locations within a virtual reality arena solely by activating and sustaining appropriate hippocampal representations of remote places. This provides insight into the mechanisms underlying episodic memory recall, mental simulation and planning, and imagination and opens up possibilities for high-level neural prosthetics that use hippocampal representations.
The patch-clamp technique and the whole-cell measurements derived from it have greatly advanced our understanding of the coding properties of individual neurons by allowing for a detailed analysis of their excitatory/inhibitory synaptic inputs, intrinsic electrical properties, and morphology. Because such measurements require a high level of mechanical stability they have for a long time been limited to in vitro and anesthetized preparations. Recently, however, a considerable amount of effort has been devoted to extending these techniques to awake restrained/head-fixed preparations allowing for the study of the input-output functions of neurons during behavior. In this chapter we describe a technique extending patch-clamp recordings to awake animals free to explore their environments.
Intracellular recording is an essential technique for investigating cellular mechanisms underlying complex brain functions. Despite the high sensitivity of the technique to mechanical disturbances, intracellular recording has been applied to awake, behaving, and even freely moving, animals. Here we summarize recent advances in these methods and their application to the measurement and manipulation of membrane potential dynamics for understanding neuronal computations in behaving animals.